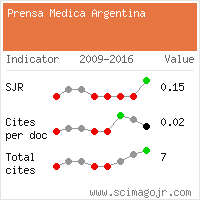
Perspective, La Prensa Medica Vol: 109 Issue: 3
Advancing Gastroenterology with Personalized Medicine Approaches
Chang Choi Ruiping*
Department of Chemistry and College of Elementary Education, Capital Normal University, Beijing, China
*Corresponding Author: Chang Choi Ruiping
Department of Chemistry and College of Elementary Education, Capital Normal
University, Beijing, China
E-mail: chang11@caas.cn
Received date: 29 May, 2023, Manuscript No. LPMA-23-107113;
Editor assigned date: 31 May, 2023, PreQC No. LPMA-23-107113 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 15 June, 2023, QC No. LPMA-23-107113;
Revised date: 22 June, 2023, Manuscript No. LPMA-23-107113 (R);
Published date: 29 June, 2023, DOI: 10.4172/0032-745X.1000167
Citation: Ruiping CC (2023) Advancing Gastroenterology with Personalized Medicine Approaches. La Prensa Medica 109:3.
Abstract
Description
In recent years, the field of medicine has witnessed a shift towards personalized approaches, recognizing the unique characteristics of each individual and tailoring treatment strategies accordingly. Gastroenterology, the branch of medicine that focuses on the digestive system, is no exception. Personalized medicine in gastroenterology involves harnessing precision approaches, such as genetic testing, biomarker identification, and targeted therapies, to enhance diagnosis and treatment outcomes. This article explores the concept of personalized medicine in gastroenterology, highlighting the potential benefits and advancements in this evolving field.
The need of personalized medicine
Traditional medical approaches often employ a "one-size-fits-all" model, where patients with similar conditions receive standardized treatments. However, individual variations in genetic makeup, environmental factors, and disease characteristics can significantly impact treatment response and outcomes. Personalized medicine aims to address this variability by tailoring medical interventions to the specific needs of each patient.
Genetic testing and gastrointestinal disorders
One of the key components of personalized medicine in gastroenterology is genetic testing. Advances in genomic technologies have enabled the identification of genetic variants associated with gastrointestinal disorders. For example, in celiac disease, genetic testing can identify individuals with specific Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) alleles, aiding in the diagnosis and risk stratification. Similarly, in hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes, such as Lynch syndrome or Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP), genetic testing can identify individuals at high risk and guide appropriate surveillance and management strategies.
Biomarker Identification for Improved Diagnosis and Prognosis: Biomarkers play a vital role in personalized medicine by providing objective measures to diagnose and monitor disease progression. In gastroenterology, biomarkers have been identified for various conditions, aiding in early detection, prognostication, and treatment response assessment. For instance, in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), biomarkers such as C-reactive protein, fecal calprotectin, and specific antibodies can assist in diagnosis, monitoring disease activity, and predicting response to therapy. In Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) levels and imaging biomarkers help in early detection and surveillance of the disease.
Targeted therapies in gastrointestinal disorders
Personalized medicine in gastroenterology also encompasses the use of targeted therapies that specifically address the molecular characteristics of a patient's disease. Targeted therapies aim to disrupt specific pathways or molecules involved in disease pathogenesis. In gastrointestinal cancers, for example, targeted therapies such as Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) inhibitors in colorectal cancer and tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) have demonstrated improved treatment outcomes in select patient populations. These therapies are often guided by the presence of specific molecular alterations identified through genetic testing or biomarker analysis.
Pharmacogenomics and individualized drug response
Pharmacogenomics is a field that investigates how genetic variations influence an individual's response to medications. By analyzing genetic variants that affect drug metabolism, efficacy, or adverse reactions, pharmacogenomics helps optimize drug selection and dosing. In gastroenterology, pharmacogenomics testing can inform the use of medications such as thiopurines or anti-TNF agents in IBD, where certain genetic variants can predict treatment response or risk of adverse events. This personalized approach minimizes trial-and-error in medication selection and reduces the likelihood of unnecessary side effects.
Challenges and future directions
While personalized medicine holds great potential in gastroenterology, several challenges need to be addressed for its widespread implementation. Access to genetic testing, cost-effectiveness, interpretation of genetic data, and ethical considerations are among the current hurdles. Additionally, further research is required to identify additional biomarkers, validate their clinical utility, and optimize treatment algorithms based on individual characteristics. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and industry stakeholders is essential to overcome these challenges and move towards more personalized and precise care in gastroenterology.
Conclusion
Personalized medicine in gastroenterology offers the potential for improved diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment outcomes. Genetic testing, biomarker identification, targeted therapies, and pharmacogenomics are revolutionizing the field, enabling tailored interventions based on individual characteristics. By considering genetic variations, disease biomarkers, and molecular pathways, personalized medicine helps optimize treatment strategies, minimize adverse events, and enhance patient outcomes. With ongoing advancements, personalized medicine has the potential to transform the landscape of gastroenterology, offering more precise and effective care for patients.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi