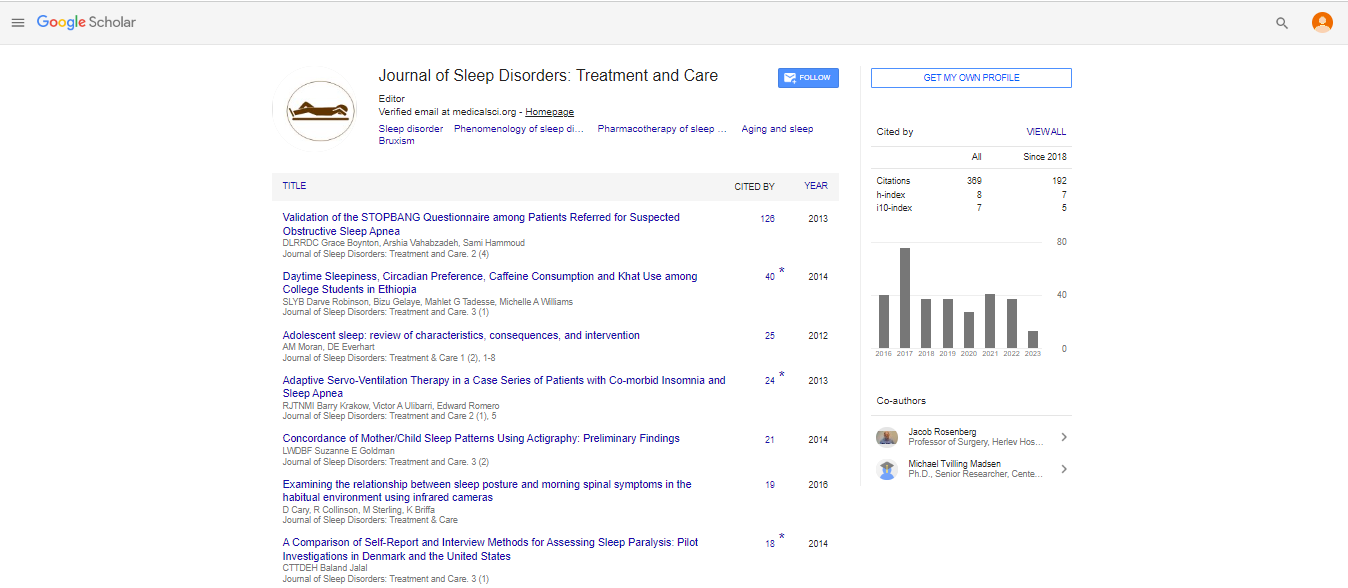
Commentary, J Sleep Disor Treat Care Vol: 2 Issue: 2
Sleep Deprivation: A Forgotten Risk Factor for Renal Dysfunction in Healthy Individuals
| Baris Afsar* |
| Konya Numune State Hospital, Department of Nephrology, Turkey |
| Corresponding author : Baris Afsar Ass.Prof of Nephrology, Ferhuniye Mah. Hastane Caddesi, 42690, Selçuklu, Konya, Turkey Tel: + (90) 332 235 45 00; Fax: + (90) 332 235 67 86 E-mail: afsarbrs@yahoo.com |
| Received: June 13, 2013 Accepted: July 12, 2013 Published: July 17, 2013 doi:10.4172/2325-9639.1000113 |
| Citation: Afsar B (2013) Sleep Deprivation: A Forgotten Risk Factor for Renal Dysfunction in Healthy Individuals. J Sleep Disor: Treat Care 2:2 doi:10.4172/2325-9639.1000113 |
Abstract
Sleep Deprivation: A Forgotten Risk Factor for Renal Dysfunction in Healthy Individuals
Typically, internal circadian clock of humans entrains to the 24-hour light-dark pattern internal where they sleep at night and are awake during the day. This pattern is maintained primarily by light exposure, which affects melatonin secretion. Dim light Melatonin onset (DLMO) is considered to be the best marker of circadian phase. Melatonin secretion normally increases at bedtime and remains high until early morning. In patients with sleep disruption, the circadian release of melatonin is impaired [1]. Experimental evidence suggest that via glutathione production, melatonin serves as an antioxidant in various tissues including the kidney [2,3]. In the same manner, melatonin protects blood vessels from adverse effects of nicotine [4], and against atherogenesis [5,6]. Melatonin also reduces interstitial renal inflammation and improves blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats [7]. A recent study has also shown that melatonin stimulates renoprotective effects of endothelial progenitor cells in acute ischemic kidney injury [8]. Thus, as a first mechanism, we hypothesize that during sleep disruption protective effects of melatonin may diminish, which may in turn result in renal dysfunction.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi