Thermodynamics of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ sorption onto low molecular weight chitosan using Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
Peter Osei Boamah
Bolgatanga Polytechnic, Ghana
: J Forensic Toxicol Pharmacol
Abstract
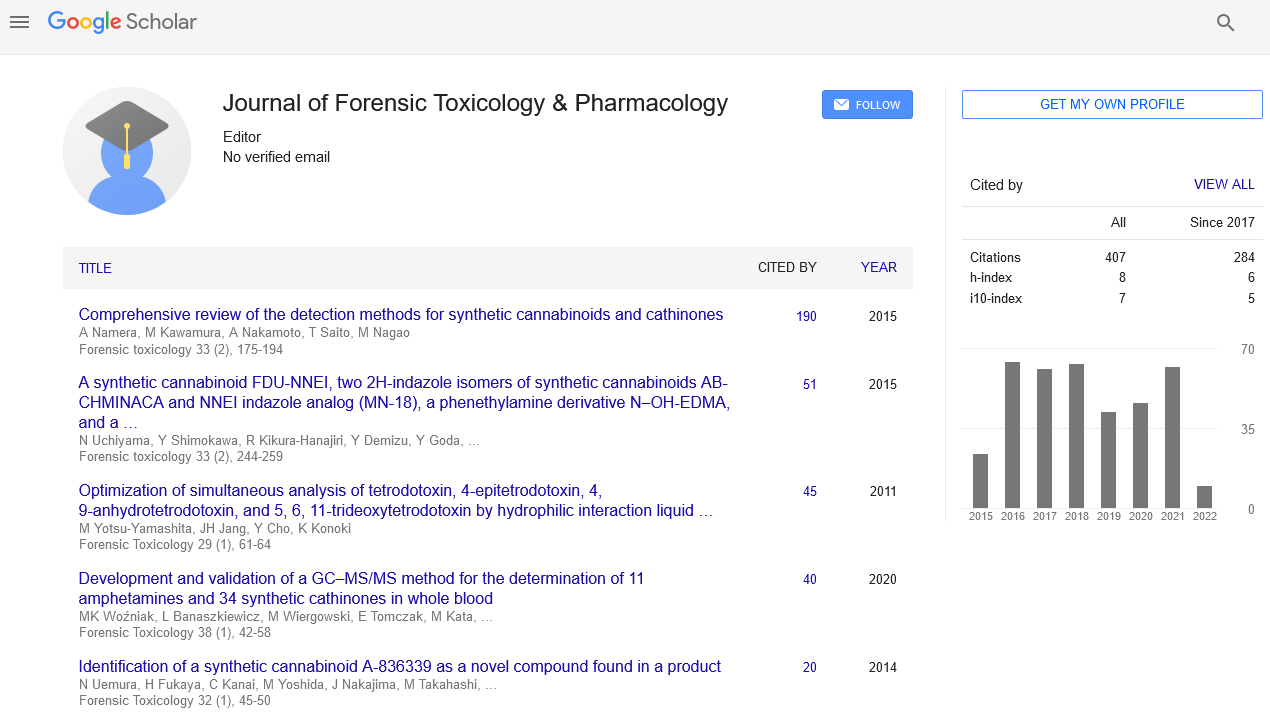
Chitosan and its derivatives possess valuable properties for its use as a sorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. In the present study, the thermodynamics of Cu2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+ sorption onto low molecular weight chitosan (CS8) using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) were investigated. Based on the ITC data, the stoichiometry data were 0.36±0.023, 0.813±0.015 and 0.029±0.006 for Cu2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+, respectively. The binding association constant (Ka) varied from (1.74±0.333)×104M-1 to (17.3±18.9)×104M-1. Also, all binding reactions to low molecular weight chitosan (CS8) were enthalpically favored and the interaction between the sorbent and the metal ions were enthalpically not driven at 25°C. Furthermore, free energy of reaction values were all determined to be negative indicating spontaneous reactions. In conclusion, the ITC instrument was successfully used to measure directly the stoichiometry (N), binding association constant (Ka), the enthalpy change (ΔH) and the entropy change (ΔS).
Biography
Email: pierrodecota@hotmail.com
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi