Research Article, Res Rep Math Vol: 1 Issue: 1
Meromorphic Functions and Theta Functions on Riemann Surfaces
Lesfari A*
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences, University of Chouaib Doukkali, Morocco
*Corresponding Author : Lesfari A
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences, University of Chouaib Doukkali, B.P. 20, 24000 El Jadida, Morocco
Tel: +212 5233- 44448
E-mail: lesfariahmed@yahoo.fr
Received: August 01, 2017 Accepted: August 20, 2017 Published: August 28, 2017
Citation: Lesfari A (2017) Meromorphic Functions and Theta Functions on Riemann Surfaces. Res Rep Math 1:1.
Abstract
Theta functions play a major role in many current researches and are powerful tools for studying integrable systems. The purpose of this paper is to provide a short and quick exposition of some important aspects of meromorphic theta functions for compact Riemann surfaces. The study of theta functions will be done via an analytical approach using meromorphic functions in the framework of Mumford. Some interesting examples will be given: the classical Kirchhoff equations in the cases of Clebsch and Lyapunov-Steklov, the Landau-Lifshitz equation and the sine-Gordon equation.
Keywords: Riemann surfaces; Meromorphic functions; Theta functions
Introduction
Let X be a compact Riemann surface of genus g ≥1 and  a square matrix of order g, symmetric and Im B > 0. We consider the Riemann theta function θ(z|B) defined by its Fourier series:
a square matrix of order g, symmetric and Im B > 0. We consider the Riemann theta function θ(z|B) defined by its Fourier series:
 (1)
(1)
Where


The convergence of this series for all  results from the fact that Im B >0. We show that this series converges absolutely and uniformly on compact sets and thus the function θ(z|B) is holomorphic over Cg.
results from the fact that Im B >0. We show that this series converges absolutely and uniformly on compact sets and thus the function θ(z|B) is holomorphic over Cg.
When the matrix B is fixed, we will put in the sequel  .Let (e1, ..., eg) be a basis of
.Let (e1, ..., eg) be a basis of  with
with  and let
and let  be the columns of the matrix B or in condensed form fj = bej, j=1, ..., g.
be the columns of the matrix B or in condensed form fj = bej, j=1, ..., g.
Theorem 1
The function θ satisfies the functional equations

 (2)
(2)
For any  we have
we have
 (3)
(3)
Any vectors of the form n + Bm is a period of the Riemann theta function, they constitute the period lattice.
Proof: The first relation results from formula (1). Concerning the second relation, we have




And, the relation (3) immediately follows.
Thus the vectors e1,..., eg are the periods of function θ(z). The vectors f1,..., fg are called the quasi-periods. The function θ is quasiperiodic and is well defined on the Jacobian variety of X.
Consider a generalization of the theta function (1) called the theta function with characteristics α and β
 (4)
(4)

To simplify the formulas, we simply note:

when the matrix B is fixed. In particular,

From equation (3), we have also

Consequently, it is sufficient to consider the functions  where
where  are such that: 0 < αj, β1< 1, j = 1, ..., g.
are such that: 0 < αj, β1< 1, j = 1, ..., g.
Theorem 2
The periodicity property of the theta-functions with characteristics is given by the following relation.

Proof
It suffices to reason as in the previous proposition.
If α1,… αg and β1,…, βg a are 0 or , we will say that the set  is a half period. In addition, a half period
is a half period. In addition, a half period  is said to be even if 4 (α, β) ≡ 0 (mod. 2) and odd if not.
is said to be even if 4 (α, β) ≡ 0 (mod. 2) and odd if not.
Theorem 3
The function  is even if half-period (z) is even and odd if half-period
is even if half-period (z) is even and odd if half-period  is odd. In addition, we have θ(z)=θ(-z).
is odd. In addition, we have θ(z)=θ(-z).
Proof: By making the substitution
z →−z, m →−m − 2,
into (4), we obtain immediately for the general term of the series,


Now, from the above definition, the sign  is determined by the parity of the number 4 (α, β), and the last relation results.
is determined by the parity of the number 4 (α, β), and the last relation results.
For example, the number of even half-periods is equal to 2g−1 (2g + 1) and of odd half-periods to 2g−1(2g − 1).
Meromorphic Functions Expressed in Terms of Theta Functions
Consider the case of Riemann surfaces of genus 1, i.e., elliptic curves. Let us recall that an elliptic function is a doubly periodic meromorphic function. In this case, the matrix B is reduced to a number that we denote by b with Im b≥0. The numbers 1 and b generate a parallelogram of the periods denoted Ω. The four theta functions corresponding to the half-periods are.
are.




These functions are holomorphic on. Moreover, we immediately deduce from theorem 3 thatθ1(z) is odd and thatθ2(z), θ3(z), θ4(z), are even. To determine the zeros of the functions θj it is sufficient, from theorem 2, to look for them in the parallelogram of the periodsΩ. Sinceθ1(z) is odd, thenθ1(0)=0 and the other zeros of θj(z) are obtained via theorem 2. In particular we see that . We claim that this zero of θ3(z), in
. We claim that this zero of θ3(z), in
Ω is unique, which is easy to prove. Namely, we need to prove that along boundary δΩ.

We have


From theorem 2, we have 
So

And


Therefore

and we have the following result:
Theorem 4
The function θ(z) has in the parallelogram of the periods Ω generated by 1 and b), only one zero at the point 
By putting z = x ∈ R, b = it, t ∈ R+, we shall see (following [16]) θ (x|it) as the fondamental periodic solution to the heat equation. Equation (1) is written

Thus θ is a real valued function of two real variables. This function is periodic with respect to x, i.e., θ(x+1|it)=θ (x|it). Since


Then

This suggests that we characterise the theta function θ(x|it) as the unique solution to the heat equation with a certain periodic initial data when t=0. To examine the limiting behaviour of f, we integrate it against a test periodic function

Then




=f(0)
Hence θ(x|it) converges, as a distribution, to the sum of the delta functions at all integral points x∈ Z as t→0. The uniqueness of this solution results from the fact that

Where δm is the distribution of Dirac at m. We have previously studied the convergence of the theta function. Thus θ(x|it) may be seen as the fundamental solution to the heat equation when the space variable x lies on a circle R/Z. Similarly, the function θ1(z) satisfies a third-order differential equation. Indeed, it is enough to use the relation.

where C is a constant  is the Weierstrass function defined by
is the Weierstrass function defined by

 is the lattice generated by two non-zero complex numbers ω1 and ω2 such that:
is the lattice generated by two non-zero complex numbers ω1 and ω2 such that:  , and take into account the differential equation:
, and take into account the differential equation:
 (6)
(6)
Where

Moreover, we have the following classical identities [1-16]:
Theorem 5
The theta function satisfies the addition formulas.

where 



where (z1, ..., z4) = (w1, ...,w4)M with

Here  are arbitrary vectors of order 2g with
are arbitrary vectors of order 2g with
 and 1 denotes the unit matrix of order g or 2g.
and 1 denotes the unit matrix of order g or 2g.
In particular, we have the formulas:


And


as well as the identity of Jacobi obtained by posing z = 0,

We shall see how to express the meromorphic functions on the torus C/Λ in terms of the theta function. Several approaches are possible:
Approach 1
Recall that any rational fraction (hence a meromorphic function on P1(C)) can be written in the form
 (7)
(7)
By analogy, let P1, ..., Pm,Q1, ...,Qm be points of the Riemann surface X and f(z) a function having zeros at the points P1, ..., Pm and poles at points Q1, ...,Qm. It is assumed that condition (i) (or what is equivalent, condition (ii)) of Abel’s theorem1 is satisfied. Since X has genus 1, then there exists a single holomorphic differential ω on X. Still according to Abel’s theorem [1], the existence of the function f(z) imposes the condition.
P1 + P2 + · · · + Pm = Q1 + Q2 + · · · + Qm
Note that for m = 1; P1 = Q1 and the only valid case is f(z)=constante. In the case where m≥2, the function f(z) may be expressed in terms of θ as follows:
 (8)
(8)
where C is a constant. This formula may be considered as the straightforward generalization of the representation (7) for the meromorphic (rational) function on P1(C). The most important difference is that in (7) the positions of the poles and zeros are arbitrary. To verify that f(z) in (8) is indeed single valued on X we have to check that f(z + 1) = f(z) and f(z + b) = f(z).
The first relation is trivial and according to relation (2) and the fact that  we also have the second relation. Thus f is doubly periodic. The function f is meromorphic with zeros in
we also have the second relation. Thus f is doubly periodic. The function f is meromorphic with zeros in  and poles in
and poles in 
Approach 2
The function log θ(z) can be expressed as the sum of a doubly periodic function of periods 1, b and a linear function. Therefore the function  is doubly periodic and meromorphic over X, with a double pole in
is doubly periodic and meromorphic over X, with a double pole in  . This function coincides with the Weierstrass function
. This function coincides with the Weierstrass function  :
:
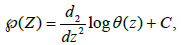 (9)
(9)
Where C is a constant chosen in such a way that Laurent’s series expansion of  en Z=0 has no constant term. The connection given by (9) between the Weierstrass function
en Z=0 has no constant term. The connection given by (9) between the Weierstrass function  and the theta function is obvious in view of
and the theta function is obvious in view of
the right-hand side (as noted above) and the information obtained above on the location of the zeros of θ(z). Now from (9) and (6) it follows that the function (z) satises a dierential equation of 3rd order.
Approach 3
Recall that meromorphic functions with simple poles on P1(C) can be written in the form

where λj∈C and C is a constant. By analogy, we consider on X the function

where Pj∈X, λj∈C such that Σjλj=0 et C is a constant. This function is doubly periodic and meromorphic with simple poles in  and residues λj at these points.
and residues λj at these points.
We have seen how the meromorphic functions on the torus C/Λ can be expressed in terms of theta function. Moreover, for g=1, we know that:  . So the construction that was done previously on the torus C/Λ or what amounts to the same on Jac(X) is also valid on the Riemann surface X. For example, let us take the case of a function having poles in P1,..., Pm and zeros in Q1, ...,Qm on the Riemann surface X. According to Abel’s theorem, we have
. So the construction that was done previously on the torus C/Λ or what amounts to the same on Jac(X) is also valid on the Riemann surface X. For example, let us take the case of a function having poles in P1,..., Pm and zeros in Q1, ...,Qm on the Riemann surface X. According to Abel’s theorem, we have

and it is possible, according to approach 1 described above, to express the function f(P) in terms of theta function using the formula

Let us now pass to the case where the surface of Riemann X is of genus g>1. Recall that the Jacobi inversion problem [5,16] consists in determining g points P1, ..., Pg on X such that:

Where (z1, ..., zg) ∈ Jac(X), (ω1,…,ωg) is a base of holomorphic differentials on X, P0 is a base point on X and L is a lattice generated by the column vectors of the period matrix. In other words, the problem is to determine the divisor in terms of z = (z1, ..., zg) 2 Jac(X) such that if ‘ is the Abel-Jacobi map, then the equation Ï�? (D) = Z is satisfied. We will study the Jacobi inversion problem using theta functions.
in terms of z = (z1, ..., zg) 2 Jac(X) such that if ‘ is the Abel-Jacobi map, then the equation Ï�? (D) = Z is satisfied. We will study the Jacobi inversion problem using theta functions.
Theorem 6
If the function defined by

is not identically zero, then it admits g zeros (counted with their order of multiplicity) on the normal representation X* of X, denoted by the symbol  , where (a1, . . . , ag, b1, . . . , bg) Is a symplectic basis of the homology group H1(X, Z). Moreover, if P1, ..., Pg denote the zeros of this function then we have on the Jacobian variety Jac(X) the formula.
, where (a1, . . . , ag, b1, . . . , bg) Is a symplectic basis of the homology group H1(X, Z). Moreover, if P1, ..., Pg denote the zeros of this function then we have on the Jacobian variety Jac(X) the formula.
 (mod. periods)
(mod. periods)
Where  is the vector of the Riemann constants defined by
is the vector of the Riemann constants defined by
 (10)
(10)
Proof:
Note that X* is a polygon with 4g sides identified in pairs. If one traverses the boundary δX*of this polygon, we notice that each side is traversed twice, one in the direction of its orientation and the other in the opposite direction. So δX* may be represented as follows

To calculate the number of zeros, we have to compute the integral (logarithmic residue):  We denote by ζ-the value of the function ζ(p) on
We denote by ζ-the value of the function ζ(p) on  and by ζ+ the value of ζ(p) on the segments aj,bj. We will use similar notations Ï�? + , Ï�? − for the Abel map Ï�? ( p) . In this notation the above integral can obviously be rewritten in the form
and by ζ+ the value of ζ(p) on the segments aj,bj. We will use similar notations Ï�? + , Ï�? − for the Abel map Ï�? ( p) . In this notation the above integral can obviously be rewritten in the form

Note that

if P∈ak and

if P∈bk. From Theorem 4, we have


Therefore (2), implies

which shows that the function ζ(p) admits g zeros on X*. To prove the second part of the theorem, we consider the integral

By designating P1, ..., Pg the zeros of the function ζ(p) and taking into account the residual theorem, we have

By reasoning as before, one obtains




Note that

Similarly, by designating by Qj (resp. Q* J ) the beginning (or end) of the contour bj, then



where  denote the columns of the matrix B. Therefore,
denote the columns of the matrix B. Therefore,

The beginning of the contour aj will be designated by Rj and its end obviously, coincides with the beginning Qj of the contour bj. We have




which ends the proof.
In general, the vector Δ depends on P0 except in the particular case g = 1, Where =  . We show that 2Δ=Ï�?−(K), where K is the canonical divisor. Hence, by skillfully choosing the point P0 we can express K in a very simple way. For example, consider the case where X is a hyperelliptic curve of genus g of affine equation.
. We show that 2Δ=Ï�?−(K), where K is the canonical divisor. Hence, by skillfully choosing the point P0 we can express K in a very simple way. For example, consider the case where X is a hyperelliptic curve of genus g of affine equation.

where all zj are distinct. Let (a1, . . . , ag, b1, . . . , bg) be a symplectic basis of the homology group H1(X, Z)) and let

the hyperelliptic involution (i.e., which consists in exchanging the two sheets of the curve X) with (aj) = −aj and σ (bj) = −bj . Note that

Then, by choosing  we get
we get



Taking into account that ωk (σP)= ωk (P) and modulo a linear combination n+Bm (a lattice generated by the column vectors of the period matrix), we obtain in this case the formula :

The zeros of a theta function on  form a submanifold of Jac(X) of dimension g − 1 called theta divisor Θ={z : θ(z) = 0}. It is invariant by a finite number of translations and can be singular. Equation (3) implies that Θis well defined on the Jacobian variety Jac(X). Since θ(z) = θ(z), we deduce that Θ is symmetric: -Θ=Θ.
form a submanifold of Jac(X) of dimension g − 1 called theta divisor Θ={z : θ(z) = 0}. It is invariant by a finite number of translations and can be singular. Equation (3) implies that Θis well defined on the Jacobian variety Jac(X). Since θ(z) = θ(z), we deduce that Θ is symmetric: -Θ=Θ.
Theorem 7
(Riemann). The function

is either identically zero, or admits exactly g zeros Q1, ...,Qg on X such that:

where Δ is defined by (10).
This result means that when we embed the Riemann surface X into its Jacobian variety Jac(X) via the Abel map Ï�?, then its image is fully include in the theta divisor, or it meets it in exactly g points. In fact, if ζ(P) is not identically zero on X, then its zeros coincide with the points P1, ..., Pg and determine the solution of the Jacobi inversion problem Ï�?(D) = z for the vector z = C −. Recall that D ∈ Div(X) is a special divisor if and only if dim L(D)≥ and dim L(K −D) ≥1where K is a canonical divisor. In the
case where D ≥ 0 a divisor is special if and only if dim Ω1(D)≠0 Note also that the special divisors of the form

coincide with the critical points of the Abel-Jacobi map,

or what amounts to the same

These critical points are the points P1, ..., PN where the rank of the differential of this application is less than g. From Riemann’s theorem 7, the function ζ(P) = θ(Ï�? (P) − C) is identically zero if and only if

where Q1 + · · · + Qg is a special divisor.
Theorem 8
Let  be a vector such that the function
be a vector such that the function

is not identically zero on X. Then the function ζ(P) admits exactly g zeros P1, ..., Pg on X which determine the solution of the Jacobi inversion problem
 where
where  i.e., the solution of
i.e., the solution of
 (12)
(12)
(recall that the symbol≡, as usual, means congruence modulo the period lattice). Moreover, the divisor D is not special and the points P1, ..., Pg are only determined from the system (12) up to a permutation.
Proof
The first assertion results from theorem 1. Moreover, the divisor  is not special because otherwise the function ζ(P) would be identically null from what precedes, which is absurd. For the last point, assume that the system (12) admits another solution Q1, ...,Qg. We will have on the Jacobian variety Jac(X),
is not special because otherwise the function ζ(P) would be identically null from what precedes, which is absurd. For the last point, assume that the system (12) admits another solution Q1, ...,Qg. We will have on the Jacobian variety Jac(X),

where L is the lattice generated by the period matrix. According to Abel’s theorem, this means that there exists a meromorphic function on X having zeros in Q1, ...,Qg and poles in P1, ..., Pg. Now we have just shown that the divisor is non-special, so such a function must be a constant, which means that Pj = Qj , j = 1, ..., g.
For example, if

is a non-special divisor on a Riemann surface X of genus g, then the function θ(Ï�?(P) – Ï�?(D)–Δ), admits exactly g zeros on X at the points P = P1, ..., Pg. We have the following characterization of the theta divisor:
Theorem 9
We have θ(C) = 0, if and only if there exists  with base point P0, such that:
with base point P0, such that:

Proof
Let us return to the function

and assume first that it is non-zero on X. By theorem 6, this function admits g zeros P1, ..., Pg on X and
 (13)
(13)
The set of these zeros being unique and as by hypothesis θ(C) = 0, then Pg = P0. Therefore Ï�?(Pg)= Ï�?(P0) and from (13), we have

Let us now turn to the case where the function ζ(P) is not identically zero on X. According to theorem 6, we have
 (14)
(14)
where Q1 +· · ·+Qg is a special divider. The latter implies the existence on X of a non-constant meromorphic function ζ having poles in Q1, ...,Qg with (P0)=0. Then,

according to the Abel theorem where P1 + · · · + Pg−1 + P0 is the divisor of the zeros of ζIt is therefore suâ�?�?cient to replace in the formula (14), Ï�?(Q1+…+ Qg), by Ï�?(P1+…+ Pg-1+ P0) while taking into account that (P0) = 0.
Theorem 10
Let D be a non-special divisor of degree g, D′ a positive divisor of degree n, a positive divisor of degree n, (ω1,…,ωg) a base of holomorphic differentials on a base of holomorphic differentials on  the Abel map with base point P0, η normalized differential of the 3rd kind 2 on X having poles on D′ and residues −1, U = (U1, ...,Ug) the vector-periods with
the Abel map with base point P0, η normalized differential of the 3rd kind 2 on X having poles on D′ and residues −1, U = (U1, ...,Ug) the vector-periods with  and finally Δ the vector defined using the Riemann constants by (10). If ψ is a meromorphic function on X having g + n poles on D + D′, then this function is expressed in terms of theta function by the formula
and finally Δ the vector defined using the Riemann constants by (10). If ψ is a meromorphic function on X having g + n poles on D + D′, then this function is expressed in terms of theta function by the formula

Proof: It should be noted that the integration contour in integrals  and
and  is the same. The function ψ (P) admits poles only on D + D′. Let us show that this function is well defined on X; i.e., it does not depend on the path of integration. In other words, it does not change when P goes through any cycle
is the same. The function ψ (P) admits poles only on D + D′. Let us show that this function is well defined on X; i.e., it does not depend on the path of integration. In other words, it does not change when P goes through any cycle  the expressions
the expressions and
and  is transformed respectively as follows:
is transformed respectively as follows:

and Moreover, using formula (4), one obtains

and the result follows from the above transformation.
On the Riemann surface X of genus g, singular functions possessing g poles and essential singularities play a crucial role in the study of integrable systems, in particular the Korteweg-de Vries equation K-dV),

the Kadomtsev-Petviashvili equation (KP),

the nonlinear Schrödinger equation

the Boussinesq equation

the Camassa-Holm equation

whose exact solutions are solitons [14], i.e., self-reinforcing solitary waves that maintain their shape as they propagate at a constant rate. We shall see by analogy from the previous theorem how to express these functions (known as Baker-Akhiezer functions) in terms of theta functions and at the same time prove their existence. Let Q1, ...,Qn be points on a Riemann surface X of genus g and zj are local parameters such that : zj(Qj) = ∞. We associate to each point Qj an arbitrary polynomial denoted by qj(zj).
Let

be a positive divisor on X and ψ(P) a function (called Baker- Akhiezer function) satisfying the following conditions :
(i) ψ(P) is meromorphic on X\ {Q1, ...,Qn} and admits poles only at the points P1, ..., Pn of the divisor D.
(ii) the function  is analytic in the neighbourhood of Qj ,j=1, ..., n.
is analytic in the neighbourhood of Qj ,j=1, ..., n.
The condition (ii) can be replaced by this condition: the function ψ admits an essential singularity of the form  at the points Qj, j = 1, ..., n where c is a constant. These functions ψ(P) form a vector space that we note L≡ L(D;Q1, ...,Qn, q1, ..., qn).
at the points Qj, j = 1, ..., n where c is a constant. These functions ψ(P) form a vector space that we note L≡ L(D;Q1, ...,Qn, q1, ..., qn).
Theorem 11
Let D = P1 + · · · + Pg be a non-special divisor of degree g. Then the space L is of dimension 1 and its basis is described using
 (15)
(15)
Where ηis a normalized differential of the 2nd kind3 having poles at the points Q1, ...,Qn, the main parts coincide with the polynomials qj(zj), where j = 1, ..., n, V = (V1, ..., Vg) with Vk= 

the Abel map with base point P0, Δ is the vector defined using the Riemann constants by (10). The integration contour in integrals  and
and  is the same.
is the same.
Proof: The function ψ1(P) has poles on the divisor D and essential singularities at the points Q1, ...,Qn. The function ψ1(P) is well defined; It does not depend on the integration path. Using the notations and reasoning similar to those of theorem 10, we obtain

and the result follows from the transformation used in the proof of the preceding theorem. Moreover, according to the Riemann- Rock theorem [5,15], the dimension of the space L is equal to deg D−g+1. As deg D=g, then the dimension of the space in question is equal to 1, which proves the uniqueness of the function with ψ1 (to a multiplicative constant). Let ψ1 ∈L be any function. Therefore, the quotient  is a meromorphic function with g(= degD) poles. The divider of the poles of
is a meromorphic function with g(= degD) poles. The divider of the poles of  coincides with the divisor
coincides with the divisor of the zeros of
of the zeros of
and we must have Ï�?(D′)-Ï�?(D)=Vy choosing the polynomials qj with sufficiently small coefficients (or what amounts to the same, the vectors of V sufficiently small), then the theta function which is in the numerator of the above expression is not identically zero. Therefore, its divisor D′ of the poles is not special and therefore  is a constant.
is a constant.
Examples
It is well known that the solutions of many integrable systems are given in terms of theta functions associated with compact Riemann surfaces. We will see below some solutions for some interesting problems.
As a first example, we consider the motion of a solid in a perfect fluid described using the Kirchhoff equations [3]:


Where,  and H is the Hamiltonian. This system has the following three first integrals:
and H is the Hamiltonian. This system has the following three first integrals:
H1=H,


Two cases can be distinguished: case of Clebsch and case of Lyapunov- Steklov. In the case of Clebsch,

with condition

The above system is written in the form of a Hamiltonian vector field. A fourth first integral is given by

where is a constant such that

The method of resolution obtained by Kötter [9] is extremely complicated and relies on an astute choice of two variables s1 and s2. Using the substitution , and an appropriate linear combination of H1 and H2, we can rewrite the above equations in the form
and an appropriate linear combination of H1 and H2, we can rewrite the above equations in the form




where A, B, C et D are constants. Let us introduce coordinates Ï�?k, ψk, 1≤k≤3 by setting

and

where


and z1, z2, z3, z4 are the roots of equation

Let s1 and s2 be the roots of equation

Where

We can express the variables p1, p2, p3, l1, l2, l3 in terms of s1 and s 2 [9]. After some algebraic manipulations, we obtain


where a, b are constants and P5(s) is a polynomial of degree five having the following form:

Consequently, the integration is done by means of hyperelliptic functions of genus 2 and the solutions can be expressed in terms of theta functions. The problem of this motion is a limit case of the geodesic flow on SO(4). Let us remind that for an algebraically completely integrable system [1], we require that the invariants of the deferential system be polynomial (in appropriate coordinates) and that the complex manifolds obtained by equating these polynomial invariants with generic constants form the afine part of a complex algebraic torus (Abelian variety) in such a way that the complex flow generated by the invariants are linear on these complex tori. Meromorphic solutions dependent on a sufficient number of free parameters play a crucial role in the study of these systems. We show [1,6] that the differential system.
in question is algebraically completely integrable and the corresponding flow evolves on an Abelian surface
where the lattice is generated by the period matrix.

The affine surface Mc defined by putting the invariants of the system equal to generic constants, can be completed into a nonsingular compact complex algebraic variety (Abelian surface)  by adjoining at in infinity a smooth curve D of genus 9. The latter is a double cover of an elliptic curve ε ramified over 16 points. The application
by adjoining at in infinity a smooth curve D of genus 9. The latter is a double cover of an elliptic curve ε ramified over 16 points. The application

is an embedding of  into
into  where (1,X1, ...,X7) forms a base of the space L(D) of meromorphic functions with at worst a simple pole along D (The functions X1, ...,X7 are expressed in a simple way as a function of x1, ..., x6). The solutions of the differential system in question in terms of theta functions are given by
where (1,X1, ...,X7) forms a base of the space L(D) of meromorphic functions with at worst a simple pole along D (The functions X1, ...,X7 are expressed in a simple way as a function of x1, ..., x6). The solutions of the differential system in question in terms of theta functions are given by

where (θ0, ..., θ7) forms a base of the space of theta functions associated with D. The two functions theta θ0, 7 are odd while the six functions theta θ1, ..., θ6 are even. In the case of Lyapunov-Steklov,


 where A, B and C are constants. A fourth first integral is given by
where A, B and C are constants. A fourth first integral is given by

where  A long and delicate calculation [10] shows that in this case too, the integration is performed using hyperelliptic functions of genus two and the solutions can be expressed in terms of theta functions. Another interesting example concerns the Landau-Lifshitz equation [2,11]:
A long and delicate calculation [10] shows that in this case too, the integration is performed using hyperelliptic functions of genus two and the solutions can be expressed in terms of theta functions. Another interesting example concerns the Landau-Lifshitz equation [2,11]:

where  and J=diag (J1, J2, J3). This equation describes the effects of a magnetic field on ferromagnetic materials. The real solutions (with magnetic anisotropy of the axis of easy magnetization type) are given by
and J=diag (J1, J2, J3). This equation describes the effects of a magnetic field on ferromagnetic materials. The real solutions (with magnetic anisotropy of the axis of easy magnetization type) are given by



Here the theta function is linked to a hyperelliptic curve of genus whose cycle
whose cycle encircles the cut [1a,a],
encircles the cut [1a,a], where the integration path crosses the cycle
where the integration path crosses the cycle  the vector
the vector  is such that : Im
is such that : Im
We cite yet another example which concerns the sine-Gordon equation [2]:

It is a non-linear wave equation with multiple applications in physics. Its solution can be written in the form


Moreover, the study of the theta functions of a Riemann surface of the genus g can be done from the point of view of tau function of a hierarchy of soliton equations [13]. The tau functions are specific functions of time, constructed from sections of a determinant bundle on a Grassmannian manifold of in definite dimension and generalize the Riemann theta functions.
References
- Adler M, van Moerbeke P, Vanhaecke (2004) Algebraic integrability, Painlevé geometry and Lie algebras, Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
- Belokolos AI, Bobenko VZ, Enol'skii VZ, Its AR, Matveev VB (1994) Algebro-Geometric approach to nonlinear integrable equations. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
- Dubrovin BA (1981) Theta functions and non-linear equations. Russ Math Surv 36: 11-92.
- Fay JD (1973) Theta functions on Riemann surfaces. Lecture notes in mathematics, Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
- Griffiths P, Harris J (1978) Principles of algebraic geometry. Wiley-Interscience, USA.
- Haine L (1983) Geodesic flow on So(4) and Abelian surfaces. Math Ann 263: 435-472.
- Igusa JI (1972) Theta-functions. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, New York, USA.
- Korotkin DA (1999) Introduction to the functions on compact Riemann surfaces and theta-functions. Exactly Solvable and Integrable Systems: 1-31.
- Kötter F (2009) Uber die Bewegung eines festen Körpers in einer Flüssigkeit. Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik 1892: 51-81.
- Kötter F (1900) Die von Steklow und Lyapunov entdeckten intgralen Fälle der Bewegung eines Körpers in einen Flüssigkeit Sitzungsber. Königlich Preussische Akad. d. Wiss. Berlin 6: 79-87.
- Landau LD, Lifshitz EM (1935) On the theory of the dispersion of magnetic permeability in ferromagnetic bodies. Phys Zeitsch der Sow 8: 153-169.
- Lesfari A (2009) Integrable systems and complex geometry. Lobachevskii J Math 30: 292-326.
- Lesfari A (2012) Algèbres de Lie affines et opérateurs pseudo-différentiels d'ordre infini. Maths report 14: 43-69.
- Lesfari A (2013) Etude des équations stationnaire de Schrödinger, intégrale de Gelfand-Levitan et de Korteweg-de-Vries. Solitons et méthode de la diffusion inverse. Aequat Math 85: 243-272.
- Lesfari A (2015) Introduction à la géométrie algébrique complexe. Hermann, Paris.
- Mumford D (1983) Tata lectures on theta I, II: Progress in Math. Birkhaüser, Boston, USA.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi