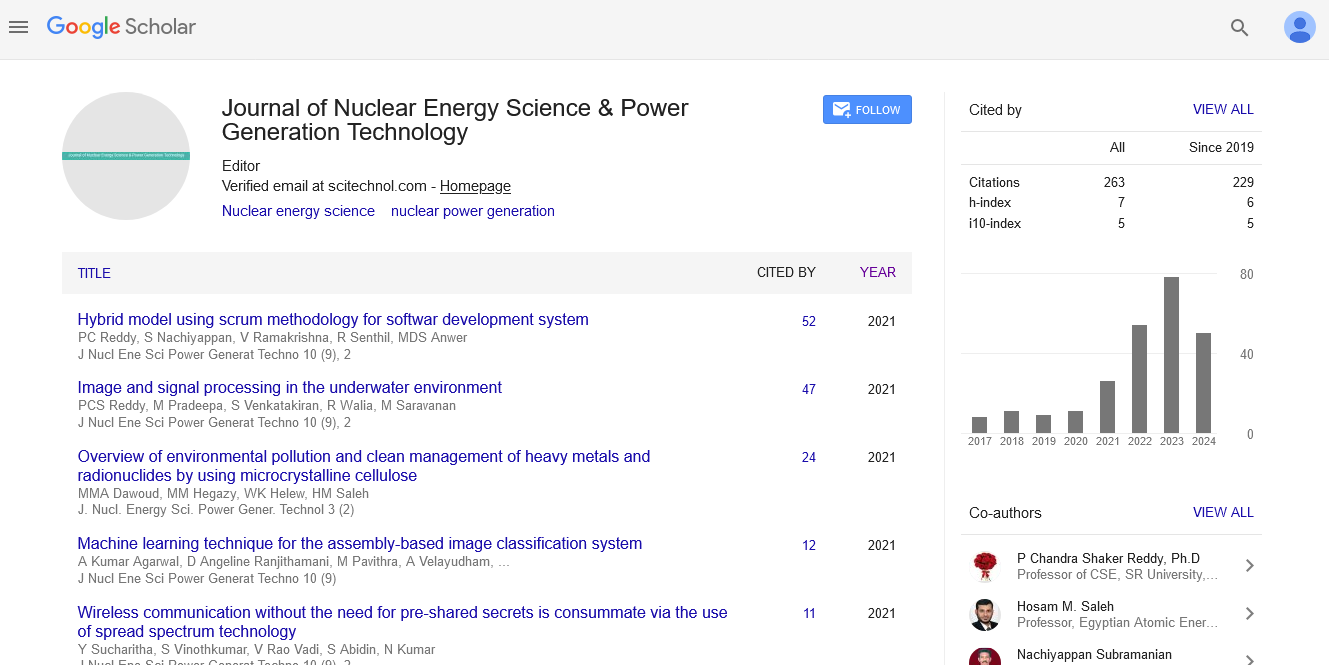
Commentary, J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol Vol: 13 Issue: 4
Integrating Energy Storage Systems with Renewable Sources for Reliable Carbon-Free Electricity
Kosiya Uri*
1Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Bangladesh Army University of Engineering and Technology, Qadirabad, Bangladesh
*Corresponding Author: Kosiya Uri,
Department of Electrical and Electronic
Engineering, Bangladesh Army University of Engineering and Technology,
Qadirabad, Bangladesh
E-mail: kosiya_uri@gmail.com
Received date: 17 June, 2024, Manuscript No. JNPGT-24-143337;
Editor assigned date: 19 June, 2024, PreQC No. JNPGT-24-143337 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 03 July, 2024, QC No. JNPGT-24-143337;
Revised date: 11 July, 2024, Manuscript No. JNPGT-24-143337 (R);
Published date: 18 July, 2024, DOI: 10.4172/2325-9809.1000405.
Citation: Uri K (2024) Integrating Energy Storage Systems with Renewable Sources for Reliable Carbon-Free Electricity. J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol 13:4.
Description
As the world deals with climate change and environmental degradation, the pursuit of carbon-free energy has become paramount. Carbon-free energy sources, which produce no Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, are essential for modifying climate change, reducing air pollution, and ensuring a sustainable energy future. This explores the various forms of carbon-free energy, their benefits, challenges, and the role they play in the global transition to clean energy. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, for electricity and transportation is the largest source of CO2 emissions. These emissions are a significant driver of global warming and climate change. To limit global temperature, rise and avoid the most catastrophic impacts of climate change, the world needs to drastically reduce its carbon footprint. Carbon-free energy sources provide a viable solution by offering clean, sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
By eliminating CO2 emissions, carbon-free energy sources significantly reduce the greenhouse gases responsible for global warming. Unlike fossil fuels, carbon-free energy does not produce air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), or particulate matter, leading to cleaner air and improved public health. Diversifying the energy mix with renewable and nuclear sources reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhances energy security. The transition to carbon-free energy produces jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research and development, stimulating economic growth.
Types of carbon-free energy
Despite the numerous benefits, the transition to carbon-free energy faces several challenges. Many renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, are intermittent. Advances in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, are essential for balancing supply and demand.
Significant investments in infrastructure, including grid modernization and the development of new transmission lines, are required to accommodate carbon-free energy.
Solar power: Solar power harnesses energy from the sun using Photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar thermal systems. PV cells convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight and produce steam for electricity generation. Abundant, renewable, and can be deployed at various scales, from small rooftop installations to large solar farms. Intermittent nature (dependent on sunlight availability), requires large land areas, and involves high initial costs.
Wind power: Wind power generates electricity by capturing kinetic energy from wind using turbines. Wind farms can be located onshore or offshore, with offshore wind farms typically experiencing stronger and more consistent winds. Renewable, scalable, and has a relatively low environmental impact. Intermittency (dependent on wind availability), visual and noise concerns, and potential impacts on wildlife.
Hydropower: Hydropower utilizes the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. It is one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy. Reliable, efficient, and can provide base-load power. Environmental impacts on aquatic ecosystems, displacement of communities, and susceptibility to droughts. Nuclear power: Nuclear power generates electricity through nuclear fission reactions, which release a significant amount of energy without producing CO2 emissions. Modern nuclear reactors are designed to be safer and more efficient. High energy density, reliable, and can provide continuous power. Radioactive waste management, high costs of plant construction and decommissioning, and public perception and safety concerns.
Geothermal energy: Geothermal energy exploits the heat from the Earth's interior to generate electricity and provide direct heating. It is typically harnessed in regions with high geothermal activity, such as volcanic areas. Reliable, low emissions, and provides base-load power. Limited to geologically suitable locations, high initial costs, and potential for induced seismicity.
Conclusion
The shift to carbon-free energy is imperative for addressing climate change and ensuring a sustainable future. By utilizing the power of solar, wind, hydro, nuclear, and geothermal energy, can significantly reduce our carbon footprint, improve air quality, and produce a resilient and secure energy system. While challenges remain, continued innovation, investment, and supportive policies will provide the way for a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world. Strong policy frameworks and regulatory support are essential to drive the adoption of carbon-free energy and ensure a level playing field for all energy sources. Gaining public acceptance for new energy projects, particularly for nuclear power and large-scale renewable installations, is vital for their successful deployment.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi