Research Article, J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol Vol: 5 Issue: 4
Implication of Removal of Cadmium Poison on Neutron Flux and Related Parameters in Nigeria Research Reactor - 1
| Anas MS1*, Ahmed YA2, Yusuf JA2 and Yahaya B3 | |
| 1CAAS Mando, Division of Agricultural Colleges, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria | |
| 2Centre for Energy Research and Training, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria | |
| 3Physics Department, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria | |
| Corresponding author : MS Anas
CAAS Mando, Division of Agricultural Colleges, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria Tel: +234 8062883863 E-mail: abuumair399@gmail.com |
|
| Received: March 26, 2016 Accepted: May 31, 2016 Published: June 04, 2016 | |
| Citation: Anas MS, Ahmed YA, Yusuf JA, Yahaya B (2016) Implication of Removal of Cadmium Poison on Neutron Flux and Related Parameters in Nigeria Research Reactor - 1. J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol 5:4. doi:10.4172/2325-9809.1000156 |
Abstract
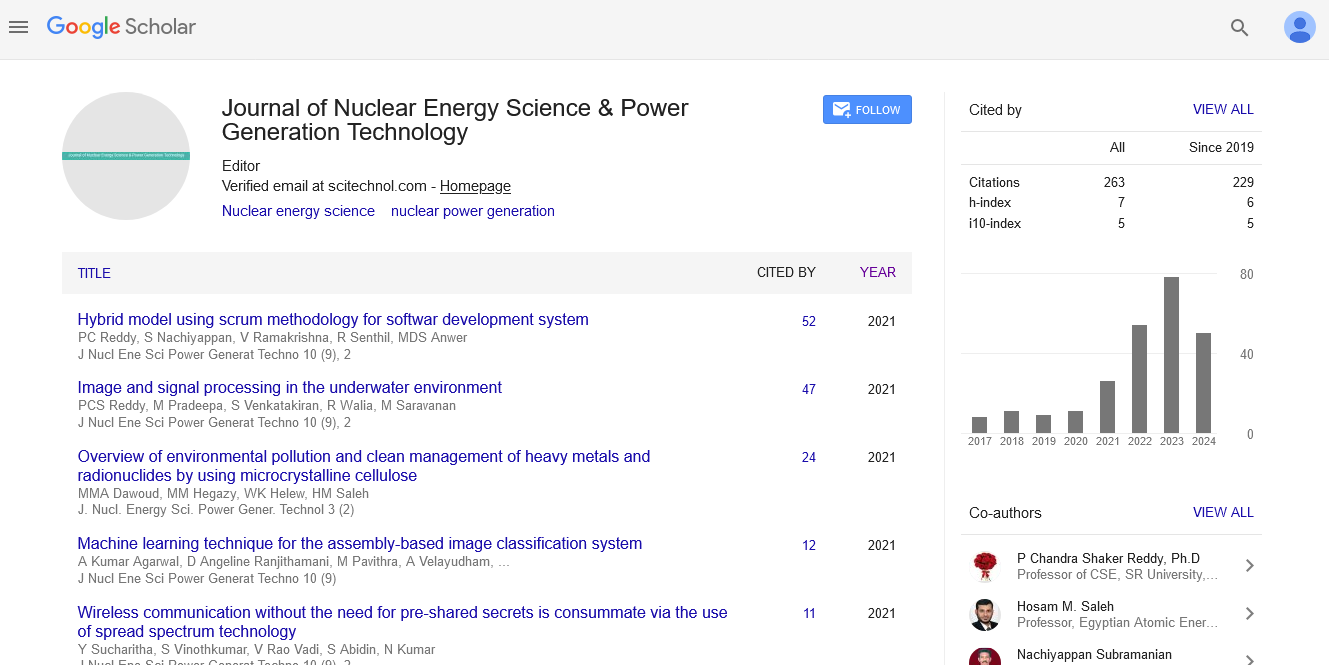
Nigeria’s Miniature Neutron Source Reactor (MNSR) has been in function since 2004. Over the ten years of operation, several installation and calculation were made on Nigeria research reactor-1 for the safety under project supply agreements and IAEA member state. In this work, we show the implication of removal of cadmium poison on neutron flux and related parameter by using lattice code WIMS and core analysis code CITATION, to automatically carry out each of the following calculations on MNSRs: core excess reactivity, verification of some safety criteria, and calculating various temperature coefficients of reactivity. Results obtained before, after and after removal of cadmium poison are: excess core reactivity (3.72, 2.96 and 2.92) mk, fuel temperature coefficient reactivity (-0.0018, -0.0054 and -0.0060) mk/°C, power coefficient of reactivity (-0.2527, -0.1260 and 0.0575) mk/kW and predicted power of (15.23, 14.65 and 14.99) kW with coolant temperature (12.43, 12.10 and 12.50) °C respectively. The result will not only boost the sample handling capabilities of NIRR-1 but will also provide useful data to the MNSR community for upgrading their reactors and specifically ageing management.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi