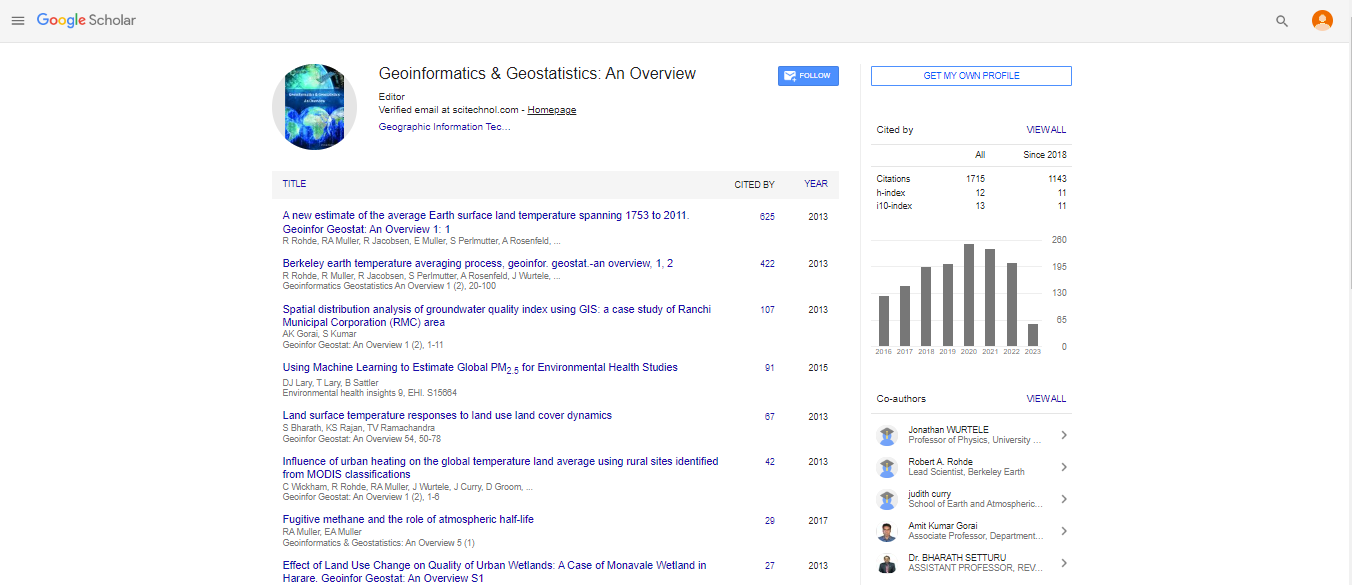
Research Article, Geoinfor Geostat An Overview Vol: 3 Issue: 2
Geostatistical Determination of Appropriate Pedotransfer Functions (PTFs) in the Estimation of Aquifers’ Hydraulic Conductivity in the Near Shore Environment of Akwa Ibom State, South-South, Nigeria
| Evans UF1*, Evans GU2 and Omotosho OO2 | |
| 1Physics and Mathematics Units, Department of Science, Maritime Academy of Nigeria, Oron, Akwa Ibom, Nigeria | |
| 2Research, Statistics, Measurement and Evaluation Unit, Department of Educational Foundations, University of Calabar, Nigeria | |
| Corresponding author : Evans UF Physics & Mathematics Units, Department of Science, Maritime Academy of Nigeria, Oron, Akwa Ibom, Nigeria E-mail: egeosystems2@gmail.com |
|
| Received: October 12, 2015 Accepted: December 02, 2015 Published: December 08, 2015 | |
| Citation: Evans UF, Evans GU, Omotosho OO (2015) Geostatistical Determination of Appropriate Pedotransfer Functions (PTFs) in the Estimation of Aquifers’ Hydraulic Conductivity in the Near Shore Environment of Akwa Ibom State, South-South, Nigeria. Geoinfor Geostat: An Overview 3:2. doi:10.4172/2327-4581.1000133 |
Abstract
Geostatistical Determination of Appropriate Pedotransfer Functions (PTFs) in the Estimation of Aquifers’ Hydraulic Conductivity in the Near Shore Environment of Akwa Ibom State, South-South, Nigeria
The study deploys six Pedotransfer Functions (PTFs) for computing hydraulic conductivity from particulate size distributions data in order to select those appropriate for determining aquifer hydraulic conductivity in the study area. Particulate size distributions at d10, d20 and d60 was obtained by subjecting 11 core samples collected at aquifer’s location during an ongoing water borehole drilling project to mechanical analysis (sieving) processes. The percentage by mass of core samples that passed each sieve was computed and plotted against the grain size distributions on a semi logarithm paper. Aquifer’s layer porosity was determined for the core samples using the imbibition technique. Hydraulic conductivity and porosity data obtained were regressed using multiple regression technique, and result statistically interpreted.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi