Research Article, J Fashion Technol Textile Eng Vol: 8 Issue: 3
Experimental Analysis of Static Thread Tension on Seam Appearance
Amir M*
Department of Textile Engineering, NED University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi Pakistan
*Corresponding Author: Amir M
Department of Textile Engineering
NED University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi Pakistan
Tel: 009233363685329
E-mail: qureshi@neduet.edu.pk
Received: June 10, 2020 Accepted: July 10, 2020 Published: July 30, 2020
Citation: Amir M (2020) Experimental Analysis of Static Thread Tension on Seam Appearance. J Fashion Technol Textile Eng 8:3.
Abstract
Investigate the impact on seam appearance due to fabric weight, bending rigidity and static thread tensions at single needle lock stitch sewing machine. The intersection among the stated parameters is crucial at stitched fabric to predict seam appearance.
Sixteen different weights of fabrics are investigated at fixed foot pressure, needle diameter, bobbin thread tension to explore the effect of intersection.
Present work is suggested that intersection of bending rigidity of fabric and thread has strong linear relationship to magnitude of static needle thread tension at lock stitched sewing machine to predict the aesthetic seam appearance of stitched fabrics.
Keywords: Seam pucker, Thread tension, Lock stitch, Bending rigidity
Introduction
In the clothing industries, fabric, sewing thread and sewing machine plays an important for the seam appearance of stitched fabrics. Influence mechanical and physical properties of sewing thread are important to predict and evaluate seam pucker Seam pucker is a crucial tool to examine the aesthetic seam appearance of stitched fabric. In the stitching of lightweight woven fabrics, bending rigidity is a tool to predict the seam appearance of a stitched fabric. It was established that fabric bending rigidity has high magnitude in comparison with sewing thread to produce balanced seam without pucker [1].
In contrast bending rigidity of sewing thread should be integrated with static sewing thread tension at sewing machine to elude seam pucker [2].
The present work is focused on the experimental exploration of fabric bending rigidity with increasing trend of static needle thread tension at single needle sewing machine on visual assessment of pucker at 80 stitched fabrics samples.
Materials and Methods
The visual assessment of pucker
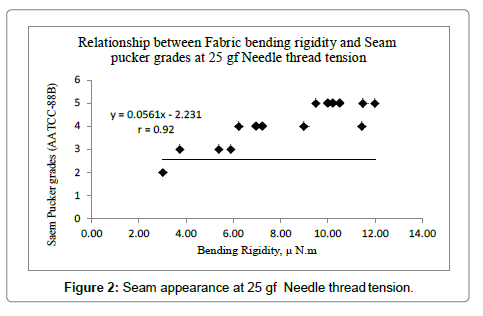
A visual assessment procedure has been developed by the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC- 88B). In this procedure, three observers compare three specimens of a particular seam with a series of five photographs of increasingly severely puckered seams, numbered 5 to 1. Grade 5 is given to a sample with no puckering while a seam with very severe puckering is graded 1. Figure 1 shows an example of the set-up of the five standards and samples of one of our experimental seams [3]. This procedure was used to assess visually the seams produced using same threads to stitch all sixteen fabrics at 25 gf, 50 gf, 75 gf 100 gf and 125 gf, i.e. there were 80 seams in all [4,5].
Properties of the experimental materials
(a) Threads: The core spun sewing thread is used which have mean diameter 0.0436 cm bending rigidity 4.1 x 10-3 gf cm2 per thread. Thread diameter was assessed microscopically at 20 points along the thread. Also the thread bending rigidities were evaluated using the KES-FB2 tester.
(b) Fabrics: The Sixteen different weight fabrics (g/m2) are used to investigate the effect of bending rigidity of fabric with increasing trend of needle thread tension while other factors kept fixed. The fabric bending rigidities (BR) were measured using the FAST-2 while the fabrics are of thin shirting hardly compressible material Table 1. gives the mean of five tests in each case [6].
Table 1: Fabric Evaluation.
| Fabric Code | Fabric weight, g/m2 | FAST-2 BR, µ N.m | Fabric Code | Fabric weight, g/m2 | FAST-2, BR, µ N.m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 68 | 3.00 | F9 | 119 | 9.00 |
| F2 | 95 | 5.38 | F10 | 120 | 10.50 |
| F3 | 100 | 5.90 | F11 | 121 | 11.44 |
| F4 | 104 | 3.74 | F12 | 124 | 10.00 |
| F5 | 109 | 6.96 | F13 | 125 | 9.50 |
| F6 | 111 | 6.23 | F14 | 126 | 11.50 |
| F7 | 115 | 7.23 | F15 | 127 | 11.50 |
| F8 | 118 | 10.21 | F16 | 130 | 12.00 |
(c) Single needle sewing Machine Setting Machine model: Fully digital, DDL9000c Machine was pre-set at the fixed settings as under:
• Sample Size=250 X 50 mm
• Speed=3000 stitchs/min
• Stitch density=5 stitches per cm
• Foot Presser pressure=5.1 kgs
• Bobbin thread tension was adjusted according to machine standard.
Fabric was made to be wrinkle free prior to stitching. Centre was marked to make sure the stitch is made at center. Total 80 samples will be investigated where sixteen fabric samples were stitches from each weight of the fabric at 25gf, 50 gf, 75 gf, 100 gf, 125 gf needle thread tension [7].
Results
The results in Tables 2a & 2b are plotted in (Figures 2-6) . All set of data exhibit a strong linear relation (the correlation coefficient in all cases), which suggests that the bending rigidity of the fabric is considered with static needle thread tension as useful measure of the tendency of a seam to pucker or elude to pucker.
Table 2: Comparison of seam puckers with visual grades.
| AATCC-88B, Seam Pucker grades at Different Needle Thread Tension | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric Code | |||||
| 25 gf | 50 gf | 75 gf | 100 gf | 125 gf | |
| F1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| F2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| F3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| F4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| F5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| F6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| F7 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| F8 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| AATCC-88B, Seam Pucker grades at Different Needle Thread Tension | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fabric Code | |||||
| 25 gf | 50 gf | 75 gf | 100 gf | 125 gf | |
| F9 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| F10 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| F11 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| F12 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| F13 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| F14 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| F15 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| F16 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
It is revealed that relative magnitude of fabric and thread bending rigidity should be considered with static tension of needle thread at sewing machine to elude seam pucker for different weight of fabrics
Conclusion
The experimental result revealed that static sewing thread tension is played an important to improve the garment seam appearance. The intersection of relative magnitude of bending rigidity of fabric and thread with static needle thread tension at sewing machine reflects strong correlation to predict the seam appearance. The presented experimental finding provides the industrial guideline to select the static needle thread tension along with fabric weight, bending rigidity to improve seam appearance.
References
- Amir M (2019) A model of seam pucker and its applications Part I: theoretical. The Journal of The Textile Institute: 1-4.
- Amir M (2017) An investigation into the measurement, prediction and elimination of seam pucker, Heriot-Watt University.
- Galuszynski S (1986) Seam Pucker, SAWTRI special publication
- Mori M, Niwa M (1994) Investigation of the performance of sewing thread. International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology 6: 20-27.
- Muhammad A(2019) A Model of Seam Pucker and Its Applications. Part II: Experimental. The Journal of The Textile Institute: 1: 60-63.
- Stylios G, Lloyd D (1989) The mechanism of seam pucker in structurally Jammed Woven fabrics. International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology 1: 5-11.
- Stylios G, Lloyd D (1990) Prediction of seam pucker in garments by measuring fabric mechanical properties and geometric relationships. International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology 2: 6-15.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi