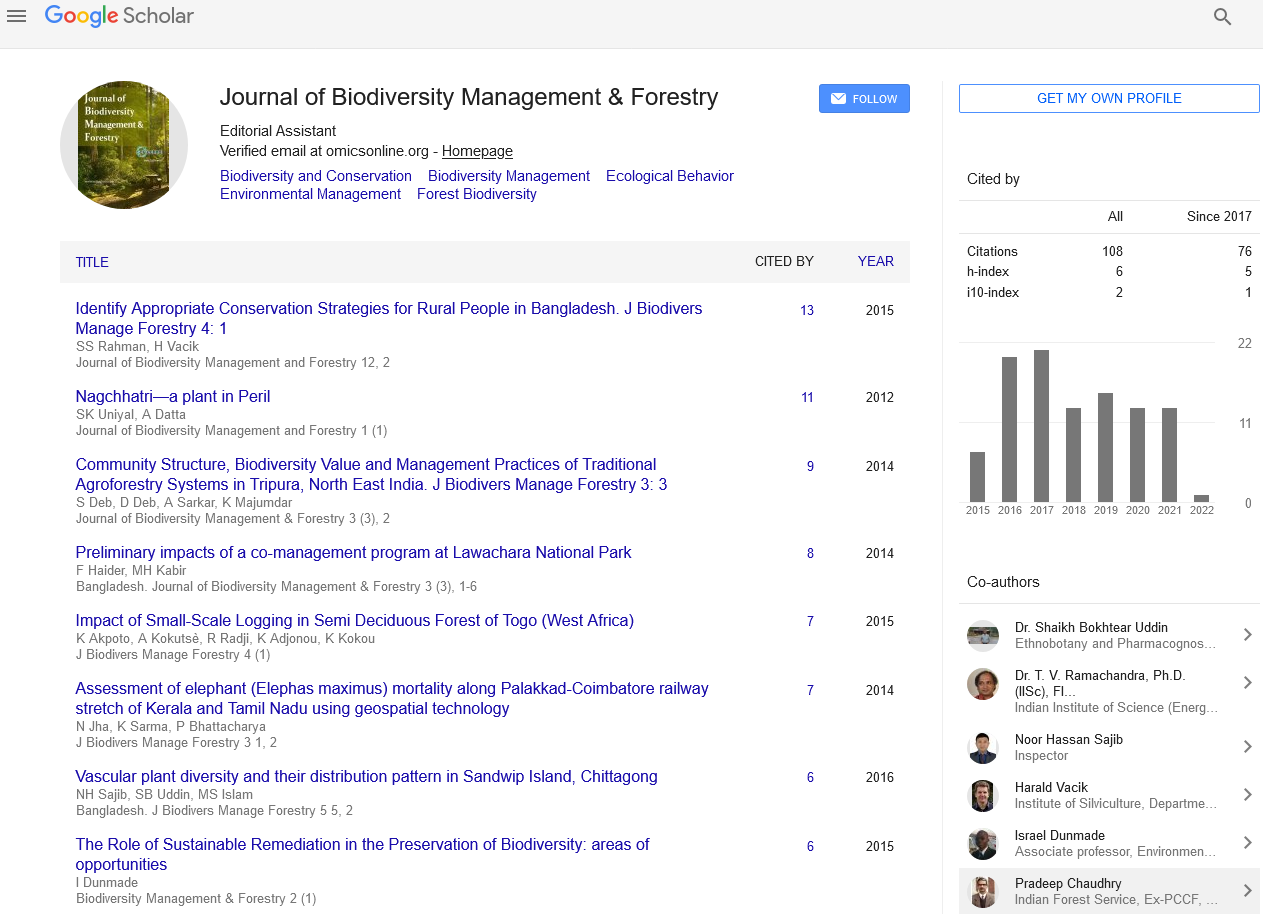
Commentary, J Biodivers Manage Forestry Vol: 10 Issue: 2
Differentiating Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Soil preservation
Abstract
Anthropogenic exercises, including petroleum derivative ignition and nitrogen (N) based compost application, have made a three five-crease increment in the statement of climatic N in the course of the only remaining century. Nitrogen affidavit is anticipated to keep on expanding 2.5-crease before the centuries over. Given that nitrogen is regularly a restricting supplement for plant development in earthbound environments, the quick expansion in nitrogen statement may effects biological system cycles and working, for example, plant development and efficiency, soil properties and the biogeochemical cycling of carbon (C). As the second biggest carbon transition in earthbound environments, soil breath assumes a significant part in worldwide and provincial carbon cycling. All out soil breath comprises of autotrophic and heterotrophic parts. Autotrophic breath gets from plant roots and its symbioses, though heterotrophic breath begins from the decay of without root soil natural carbon and litter by organisms and fauna. Past investigations utilizing nitrogen expansion tests have analyzed what changes in nitrogen accessibility mean for these RS segments.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi