Research Article, J Comput Eng Inf Technol Vol: 13 Issue: 4
Creating Smart Campus: The Future University Campus Based on IoT and Global Positioning System (GPS)
Trezah Iftikhar*
1Department of Systems and Technology, University of Management and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan
*Corresponding Author: Trezah Iftikhar,
Department of Systems and Technology,
University of Management and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan
E-mail: trezah.iftikhar@gmail.com
Received date: 26 June, 2024, Manuscript No. JCEIT-24-139901;
Editor assigned date: 28 June, 2024, Pre QC No. JCEIT-24-139901 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 15 July, 2024, QC No. JCEIT-24-139901;
Revised date: 23 July, 2024, Manuscript No. JCEIT-24-139901 (R);
Published date: 31 July, 2024, DOI: 10.4172/2324-9307.1000306
Citation: Iftikhar T (2024) Creating Smart Campus: The Future University Campus Based on IoT and Global Positioning System (GPS). J Comput Eng Inf Technol 13:4.
Abstract
The huge revolution in the IT industry has impacted our surroundings greatly. Our environments are now smarter than ever. Security monitoring has also been revolutionized through use of Global Positioning System (GPS) and other advanced monitoring technologies including Google Maps API and high end location sensors. GPS represents an embedded technology that is used in smartphones to gather information related to location of different objects in our surroundings. The information is then analyzed and the results which are of great importance are also backed up at the cloud server, are then communicated to target users and used through the smart devices using smart applications. The devices that are IP enabled and are interconnected through the common connection point “the web” as a whole, called IoT or the internet of things. The proposed research indicates the use of Google Maps API in combination with IoT to design a smart campus model that is used to communicate and share location information among its users, and is secure. The shared location information is used by the proposed model for an automated attendance management system. The smart campus model is implemented and tested using an android Integrated Development Environment (IDE). The proposed smart campus environment is beneficial in terms of information accessibility and secure communication on campus.
Keywords: Global Positioning System (GPS); Google Maps
API; Internet of Things (IoT); Android Integrated Development
Environment (IDE); Smart campus
Introduction
In recent years, the growth in the IT industry has shaped our lifestyle in a very different manner and changed our communication and living standards greatly. The major impact took place with the revolution in mobile phone and telecommunication industry with the development of smart devices and wireless internet access.
Smartphones using GPS sensors that are embedded in the device, are being vastly used for location sensing and for enabling Location Based Services or commonly known as LBS.
LBS is a wireless service that determines the location information of the information device (mobile) user by using Geographical Information System (GIS) and other satellite navigation platform.
The Control plane Locating is used in devices that do not have embedded GPS equipment. It gets the location based on the radio signal delay of the mobile-phone tower that is at the shortest distance from the object. It is an obsolete technique for location sensing and is typically used in phones without the integrated A-GPS chips.
Network Load Balancing System (NLBS) involves technologies such as Bluetooth low energy, Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), infrared and/or Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)/Near field communication technologies, which are used to match devices to nearby services. This application allows a person to access information based on their surroundings; especially suitable for using inside closed premises, restricted or regional areas. Another alternative is an operator and GPS-independent location service.
In the past decade, the Global Positioning System has been very famous for location sensing in smart environments including Smart cities and smart hospitals etc. Another major use of GPS is seen in security monitoring or surveillance. The information on campus, gathered by GPS on smart devices is of great use in smart environments and is used to make decisions in smart systems. Cloud computing is another major advancement of the century that came into limelight when Google used it to get the benefit of distributed resources for their storage and processing needs.
Google Maps is a major breakthrough in terms of location sensing and location information sharing in the world of smart devices. It is a mapping service provided over the web by Google.inc. It was launched as a desktop application back in 2004. Google launched its Maps API for common use in 2005. The Maps API is a platform to be used by developers to include Google maps into their Web and mobile applications for location sensing and many other location related activities.
The main purpose of the proposed research is to develop a smartphone application for Students and teachers in a university for sharing location information among teachers and students, making a way of communication between the teachers and students. The teachers may be able to view the student’s location through a smart phone application and will be able to send updates regarding classes and courses to the enrolled students. The students will be able to share their location information and view the updates sent by the teacher.
Smart environment is a collective functioning collaboration of many technologies. The front end of the environment is controlled by different smart devices with smart applications running on them. The components or the members of the environment are sensed and monitored and controlled by wireless sensors that are planted in the form of a wireless network within the environment. The back end of the environment is working on a cloud computers network. That provides cloud based storage and processing facilities to the users. Smart homes have been a major field of research in the past decade.
Literature review
Smart environment is a collective functioning collaboration of many technologies. The front end of the environment is controlled by different smart devices with smart applications running on them. The components or the members of the environment are sensed and monitored and controlled by wireless sensors.
A model for smart homes using a sensor based network [1]. It analyzed the existing solutions and platforms for smart homes and examined them for security challenges and threats and a detailed report has been presented, describing the challenges in detail, in the later part of the paper. The key elements of the smart network include smart light bulb, cell phone, routers, smart door lock and many other smart appliances being controlled by smart devices.
On the other hand, presented a detailed analysis for security provided by a smart home platform called “Smart things” [2]. “Smart things” is a popular smart home concept, owned by Samsung. It has the largest number of online applications available for smart home systems working currently. The applications are compatible with a large number of smart devices.
The Cloud Computing and RFID technologies to build a plant factory and realized automatic controlled production of agriculture [3].
On the other hand, also described how cloud computing and IoT can be used together to overcome the big data issues [4]. The paper also illustrates a new kind of cloud service called “sensing as a service”. A model that used the RFID and ZigBee sensing techniques for tracking objects in real time [5].
A system for monitoring behavioral information of the patient in a smart home [6]. The information was collected in a very transparent manner and then can be shared with the doctors or any other medical personnel. A system that was used for the implementation of a smart city framework using IoT [7]. Network architecture for monitoring condition inside a home the paper used low cost sensor network for monitoring. The network is implemented through IoT [8].
A sensor based network to implement a smart city environment [9]. The smart heterogeneous sensors network is implemented and aimed to detect anomalous activities like theft etc. The smart network was tested in a test bed and was useful for security monitoring. A smart system for monitoring lawns [10]. The system used an RGB scan to monitor the color and quantity of grass in the lawn. The system used for lawn monitoring consisted of 120 heterogeneous Sensors for sensing the environment. Providing very satisfactory results with a reduced amount of resources used.
An interesting smart solution for the university campus’s car parking which is essentially a part of a smart campus [11]. The smart car parking system is a three tier smart system including a smart user interface based on android mobile application development platform.
A smart school bus monitoring system [12]. The system monitors and controls the school bus as it travels along school children, the system is able to monitor the speed, route and location etc. The students are identified when they board the bus through RFID tags. GPS has been used to monitor location information which is then shared with school management and parents through a mobile application.
Methodology
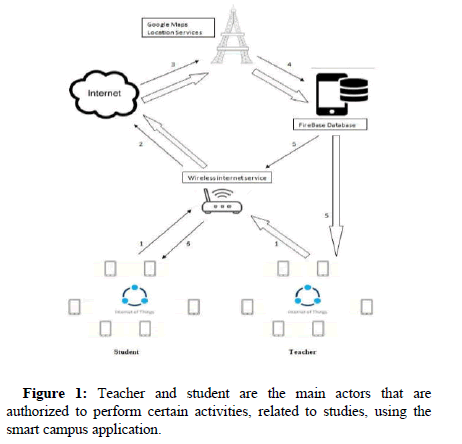
The proposed system uses the medium of IoT for performing the specified tasks and activities [13]. The proposed system is based upon an android application for performing location related activities by students and teachers. The working of the proposed system is shown in the figure below. The figure shows the complete cycle of information flow, for the proposed system on a larger scale: The main purpose of developing the smart campus application is to develop a system for the students of university, to perform activities related to their academics through the ease of a touch on their smart devices [14].
The complete architecture and working of the proposed system is visible. The proposed system consists of Smart devices or smart phones as key factors in the proposed framework in Figure 1.
Assumptions
The following assumptions must be true in order for the developed system to perform accurately. The conditions must be fulfilled in order to be using the system to its full capacity [15]. The developed system may not perform accurately, or according to its full capacity, if the following conditions are not met [16]. The conditions are explained in detail in the following section of the chapter.
• Each condition is a prerequisite for deploying the developed system into the practical vicinity, and holds great impact upon the performance of the system.
• The classroom, in which the attendance management system will be performing, must be a perfect square room.
• The Teacher using the smart campus attendance management system, must be present at the center of the classroom. In order to mark the attendance, the smart device using attendance management system is present at the center of the square room.
• The mobile device from which the student is logged in, is possessed by the authorized student only, at all times.
• The students have not shared their login ID and passwords with other students and students have not logged in from other student’s smart devices.
• The system considers the location of the smart device as the location of the student, therefore all the students have their mobile phones present with them
• The students are logged into the smart campus application and have turned on their location permission for the smart campus.
Components overview
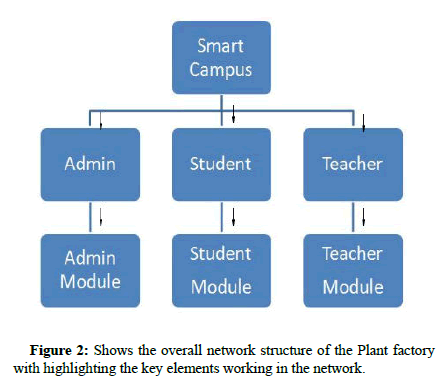
The smart campus is a smart phone application that has been designed to be used within the campus by the admin, students and teachers of university [17]. The app allows the students to share their information with the teachers and the teachers to communicate with the students through the application interface [18]. The students will be able to view and share their location information to the teacher and only the authorized teachers will be able to view the student’s location information in Figure 2.
High Level Components
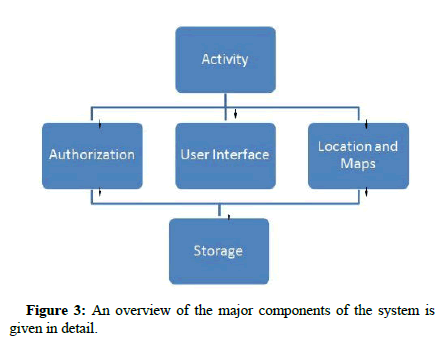
The high level design components are of great importance in understanding the overall functionalities of the proposed system [19]. An overview of the major components of the system is given in detail.
The design of the high level components forms the backbone of the system. The high level components define the major functionality of the proposed system [20]. The overall network structure of the Plant factory with highlighting the key elements working in the network shown in Figure 3.
Performance and limitations
We provide an experimental evaluation here to evaluate the proposed thesis application by measuring the performance of the proposed system. The language used in this thesis for implementation is “Java” [21-25]. The code of the Smart campus application is compiled on Android studio. The android device used for testing the proposed system is Samsung galaxy grand neo plus.
In experiment 1, the proposed system was tested against its claim for the teacher to view its enrolled student’s location information using the smart campus application interface for teachers. The experiment will be performed on the previously specified smart device to view and save the student location using a Google map on the application’s teacher module.
In experiment 2, the proposed system was tested against its claim for the teacher to mark attendance for its enrolled students, using the smart campus application interface for teachers [26,27]. The experiment were performed on the previously specified smart device to mark and view the student attendance using the attendance feature on the application’s teacher module.
Comparison of our proposed model with other similar models
The following table is the comparison of the proposed model with two other similar model frameworks [28-30]. The proposed framework has provided improved facilities of location sensing within and outside the building, automated attendance management system, message based communication between the system actors (Students and teachers) and smooth information access by only authorized users using secure ways of centralized data storage and sharing among authenticated users (Table 1) [31-35].
| Features RFID tag detection using smart antenna for tag based school monitoring system |
RFID tag detection using smart antenna for tag based school monitoring system | IoT based smart school bus monitoring and notification system | Proposed model of smart campus using IoT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location sensing within the building | Yes | No | Yes |
| Location sensing outside the building | No | Yes | Yes |
| Need of additional hardware including scanners or readers for location sensing | Yes | Yes | No |
| Interactive user interface through mobile application | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Centralized data storage and sharing | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Message based communication through mobile application interface | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Authentication and authorization | No | Yes | Yes |
| Real-time data sharing | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Automated attendance management using location information | Yes | No | Yes |
Table 1: Information access by only authorized users using secure ways of centralized data storage and sharing among authenticated users.
Thus from Table 1 it is evident that the proposed smart campus model is providing similar in fact more advanced facilities within the university environment without the hassle of installing additional hardware or network components including motion sensors, RFID scanners etc., [36-39]. The proposed system thus proves to be more cost effective and practically feasible solution for location sensing need within the university environment [40-47].
The benefits of the proposed model
• By using the proposed model, the admin staff will be able to use the application to add, view, update and delete the courses. Student and teacher profiles can also be added, updated, viewed and deleted.
• By using the proposed model, the teachers will be able to view their enrolled student’s profile and location information.
• By using the proposed model, the teachers may be able to send any updates regarding the course, to the enrolled students.
• By using the proposed model, the teachers may be able to mark attendance of their enrolled students using the shared location information of students.
• By using the proposed model, the teachers and students will be able to communicate through text messages.
• By using the proposed model, the students will be able to view the updates sent by their teachers.
• By using the proposed model students will be able to view the detailed information of their enrolled courses and teachers.
• By using the proposed model, the students will be able to view and share their location information.
The limitations of the proposed model
• The proposed system used firebase online real-time database which is a non-relational database. It uses a tree-like structure to store data in the form of nodes and Childs.
• The Firebase database uses the online real-time storage to store database schema and data. The data retrieval speed may vary due to fluctuation in internet speed.
• The proposed system uses an approximate value of longitude and latitude of the student’s device, to mark the location of the student on a map. The stored values may give a slight different location result as compared to the actual location.
• The system considers the location of the device from which the student logs into the system as the student’s location. The assumption may become false under certain circumstances i.e. loss or theft of mobile devices.
• The system used a radius of 30 meters to mark the student as present. If the student’s distance from the teacher’s location is more than 30 meters. It will be marked absent.
Future work
The proposed thesis is developed as a beginner application for university campus.
It can be further developed to provide a richer user experience. The user information can be shared among users through a centralized storage over a network. This would help in centralized storage and access to the information resources.
The developed thesis application assumes that a classroom is a perfect square and the teacher must be present at the center of the classroom with the mobile device to mark the attendance of the students. The future version of the developed thesis may work in classrooms that are nor perfectly square shaped and are rectangular. The future versions of the developed smart campus application may allow the teacher to mark the attendance of students from any part of the classroom rather than the center of the room.
Conclusion
The motivation of this thesis project is to build an application framework, for providing a simple platform for better communication among students and teachers. By using Android SDK and Android Studio IDE as the development environment the proposed thesis framework application is built keeping in mind about the design standards and maintainability of the code.
The designed smart campus application makes use of GPS, Google maps API and location features of the Android device to provide a rich user experience to the students and teachers, enabling them to view the location information.
References
- Lee C, Zappaterra L, Choi K, Choi AH (2014) Securing smart home: Technologies, security challenges, and security requirements. IEEE CNS 20(6): 67–72
- Fernandes E, Jung J, Prakash A (2016) Security analysis of emerging smart home applications. IEEE CNS 636–654.
- TongKe F (2013) Smart agriculture based on cloud computing and IOT. Journal of Convergence Information Technology. J Converg Inf Technol 8(2): 210–216.
- Rao BBP, Saluia P, Sharma N, Mittal A, Sharma SV (2012) Cloud computing for Internet of Things & sensing based applications. Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensing Technology. IEEE CNS 374–380.
- Alharbe N, Atkins AS, Champion J (2015) Use of cloud computing with wireless sensor networks in an internet of things environment for a smart hospital network. eTELEMED 52-58
- Helal A, Cook DJ, Schmalz M (2009) Smart home-based health platform for behavioral monitoring and alteration of diabetes patients. J Diabetes Sci. Technol 3(1): 141–148.
- Jin J, Gubbi J, Marusic S, Palaniswami M (2014) An information framework for creating a smart city through internet of things. IEEE CNS 1(2): 112–121.
- Dieter S, Suryadevara NK, Mukhopadhyay SK (2013) Towards the Implementation of IoT for Environmental Condition Monitoring in Homes. IEEE CNS 13(10): 67–69.
- Filipponi L, Vitaletti A, Landi G, Memeo V, Laura G et al. (2010) Smart city: An event driven architecture for monitoring public spaces with heterogeneous sensors. IEEE CNS 281–286.
- Marin J, Rocher J, Parra L, Sendra S, Lloret J et al. (2018) Autonomous WSN for lawns monitoring in smart cities. IEEE CNS 501–508.
- Ji Z, Ganchev I, O'Droma M, Zhao L, Zhang X (2014) A cloud-based car parking middleware for IoT-based smart cities: Design and implementation. Sensors 14(12).
- Raj JT, Sankar J (2018) IoT based smart school bus monitoring and notification system. IEEE CNS 89–92.
- Ahmed MM, Banu S, Paul B (2018) Real-time air quality monitoring system for Bangladesh’s perspective based on Internet of Things. 1–5.
- Ali I, Asif M (2018) Applying security patterns for authorization of users in IoT based applications. 1–5.
- Almulhim M, Zaman N (2000) His academic achievements further extended with PhD in Information Technology at University Technology Petronas (UTP) Malaysia.
- Alshattnawi SK (2018) Smart water distribution management system architecture based on internet of things and cloud computing. IEEE CNS 289–294.
- Broujeny RS, Madani K (2017) A multi-layer system for smart-buildings’ functional and energy-efficiency awareness. IEEE CNS 87–92.
- Cho Y, Kim M, Woo S (2018) Energy efficient IoT based on wireless sensor networks. IEEE CNS 294–299.
- Corredor I, Iglesias J, Bernardos AM, Casar JR (2012) A development methodology to facilitate the integration of Smart Spaces into the Web of Things. Sensors 12(7): 829–834.
- Darianian M, Michael MP (2008) Smart home mobile RFID-based internet-of-things systems and services. IEEE CNS 116–120.
- Elhoseny M, Gonzalez RG, Abu-Elnasr OM, Shawkat SA, Arunkumar N (2018). Secure Medical Data Transmission Model for IoT-Based Healthcare Systems. IEEE CNS 6.
- Han DM, Lim JH. (2010) Smart home energy management system using IEEE 802.15.4 and zigbee. IEEE CNS 56(3): 1403–1410.
- Hou Z, Chen Y (2018). A real time vehicle collision detecting and reporting system based on Internet of Things technology. IEEE CNS 1135–1139.
- Hussain B, Hasan QU, Javaid N, Guizani M, Almogren A (2018) An Innovative Heuristic Algorithm for IoT-Enabled Smart Homes for Developing Countries. IEEE CNS 6: 15550–15575.
- Jerald V, Rabara A, Premila D (2015) Internet of Things (IoT) based Smart Environment integrating various Business Applications. IEEE CNS 128(8): 32–37.
- Khanam S, Mahbub M, Mandal A, Kaiser MS, Mamun S (2014) Improvement of RFID tag detection using smart antenna for tag based school monitoring system.
- Lama TA, Reyes BH (2004) Doctors and hospitality industry. Revista Medica de Chile. 132(2): 265–268.
- Li B, Hathaipontaluk P, Luo S (2009) Intelligent oven in smart home environment. IEEE CNS 247–250.
- Li M, Lin HJ (2015) Design and implementation of smart home control systems based on wireless sensor networks and power line communications. IEEE CNS 62(7): 4430–4442.
- Li W, Logenthiran T, Phan VT, Woo WL (2018) Implemented IoT-based self-learning home management system (SHMS) for Singapore. IEEE CNS 5(3): 2212–2219.
- Mall S, Gupta M, Chauhan R (2018) Diet monitoring and management of diabetic patient using robot assistant based on Internet of Things. IEEE CNS 1–8.
- Nath RK, Bajpai R, Thapliyal H (2018) IoT based indoor location detection system for smart home environment. IEEE CNS 1–3.
- Nathalie M, Symeon P, Antonio P, Kishor ST (2012) Combining cloud and sensors in a smart city environment. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 1–10.
- Novitskaya YV, Strekalovskiy SA, Gavrilov AV (2015) Event monitoring system of smart school laboratory. IEEE CNS 116–119.
- Oshin TO, Poslad S, Ma A (2012) Improving the energy-efficiency of GPS based location sensing smartphone applications. IEEE CNS 1698–1705.
- Pandey J, Kazmi SIA, Hayat MS, Ahmed I (2018) A study on implementation of smart library systems using IoT. IEEE CNS 193–197.
- Panth S, Jivani M. (2011) Home Automation System (HAS) using Android for Mobile Phone. IJECSE 4(25): 4844–4849.
- Pham TN, Tsai MF, Nguyen DB, Dow CR, Deng DJ (2015) Special section on emerging cloud-based wireless communications and networks a cloud-based smart-parking system based on internet-of-things technologies. IEEE CNS 1581–1591.
- Polycarpou AC, Samaras T, Sahalos JN (2014) An RFID-based library management system using smart cabinets: A pilot project. IEEE CNS 2954–2955.
- Rahim MH, Khalid A, Javaid N, Alhussein M, Aurangzeb K, Khan ZA (2018) Energy efficient smart buildings using coordination among appliances generating large data. 6: 34670–34690.
- Sikder AK, Acar A, Aksu H, Uluagac AS, Akkaya K (2018) IoT-enabled smart lighting systems for smart cities. IEEE CNS 639–645.
- Tamgno JK, DIallo NR, Lishou C. (2018) IoT-based medical control system. IEEE CNS 399–404.
- Tian Y, Zheng, B, Li Z (2018) Agricultural greenhouse environment monitoring system based on Internet of Things. IEEE CNS 2981–2985.
- Sivasankaran VS, Muruganand AP (2013) Advanced Embedded System Assisted Gsm and Rfid Based Smart. IEEE CNS 2(7): 3124–3128.
- Viani BF, Ieee M, Robol F, Polo A, Rocca P (2013) Wireless architectures for heterogeneous sensing in smart home applications: Concepts and real implementation. IEEE CNS 101(11): 2381–2396.
- Xu J, Lee YH, Tsai WT, Li W, Son YS (2009) Ontology-based smart home solution and service composition. 297–304.
- Zhu C, Leung VCM, Shu L, Ngai ECH (2015) Green Internet of Things for a Smart World. IEEE CNS 3: 2151–2162.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi