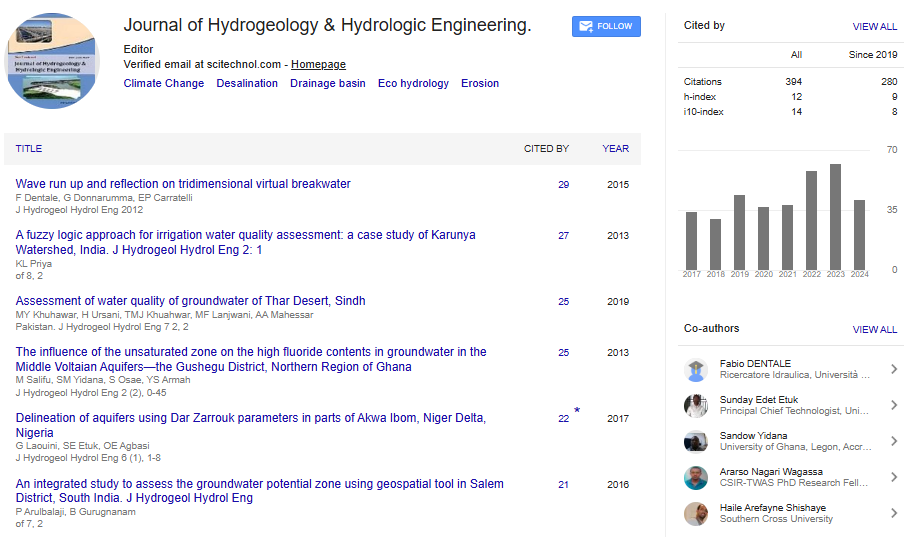
Perspective, J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng Vol: 13 Issue: 6
Assessing Water Quality for Human Health and Sustainable Ecosystems
Emily Johnson*
1Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
*Corresponding Author: Emily Johnson,
Department of Civil and Environmental
Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
E-mail: johnsone38@gmail.com
Received date: 26 November, 2024, Manuscript No. JHHE-24-154121;
Editor assigned date: 28 November, 2024, PreQC No. JHHE-24-154121 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 12 December, 2024, QC No. JHHE-24-154121;
Revised date: 20 December, 2024, Manuscript No. JHHE-24-154121 (R);
Published date: 27 December, 2024, DOI: 10.4172/2325-9647.1000351.
Citation: Johnson E (2024) Assessing Water Quality for Human Health and Sustainable Ecosystems. J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng 13:6.
Description
Water quality is a precarious aspect of environmental sustainability and public health, influencing ecosystems, agriculture and human activities. It encompasses the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of water, determining its suitability for various uses. This article explores the factors affecting water quality, methods for assessment and strategies for improvement.
Water quality can vary due to natural processes and human activities. Some natural factors include geological formations, weather patterns and biological activity in aquatic systems. However, humaninduced factors like industrial discharge, agricultural runoff and urbanization significantly contribute to water quality degradation.
Pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides and nitrates from farming practices often seep into water bodies, leading to contamination. Similarly, untreated sewage and industrial waste introduce harmful pathogens and chemicals into water sources. Climate change improves these issues by altering rainfall patterns, increasing water temperatures and affecting the natural purification capacity of water bodies.
Methods for assessing water quality
Water quality assessment is essential for monitoring and management. Various parameters are measured, including:
Physical parameters: These include temperature, turbidity and color. Elevated temperatures can reduce oxygen levels, affecting aquatic life, while high turbidity indicates suspended particles, which may carry pollutants.
Chemical parameters: These involve pH, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and the presence of specific ions like nitrates and phosphates. High BOD levels indicate organic pollution, while low DO levels signify poor water quality.
Biological parameters: Biological assessments include the presence of microorganisms such as bacteria and algae. The detection of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and other pathogens often indicates contamination by human or animal waste.
Advanced technologies such as remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are now employed to provide comprehensive water quality data, aiding in effective management and policy-making.
Importance of maintaining water quality
Maintaining good water quality is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it supports biodiversity by providing a healthy habitat for aquatic organisms. Polluted water disrupts ecosystems, causing species decline or extinction.
Secondly, water quality impacts human health. Contaminated water can lead to diseases like cholera, diarrhea and hepatitis. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), poor water quality is a leading cause of illness in developing countries.
Lastly, clean water is essential for agriculture and industry. Irrigating crops with polluted water can introduce toxins into the food chain, posing long-term health risks. Similarly, industries relying on water for production may face operational challenges if water quality standards are not met.
Strategies for improving water quality
Several measures can be implemented to improve and sustain water quality:
Pollution control: Reducing industrial discharge and promoting eco-friendly farming practices can minimize water contamination. Enforcing regulations to limit the use of harmful chemicals is equally important.
Wastewater treatment: Investing in wastewater treatment plants ensures that sewage and industrial effluents are treated before being discharged into water bodies.
Community awareness: Educating communities about the importance of water conservation and proper waste disposal can significantly reduce pollution at the source.
Reforestation and wetland restoration: These natural methods enhance water purification by filtering pollutants and maintaining hydrological balance.
Regular monitoring: Periodic assessment of water quality helps identify contamination sources and enables timely interventions.
Conclusion
Water quality is a basis of environmental health and human development. As the global demand for water rises, ensuring its quality becomes even more precarious. By addressing pollution sources, investing in advanced treatment technologies and development community engagement, we can protect water resources for future generations. Sustainable water management practices are not just a necessity but a collective responsibility to preserve this invaluable resource.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi