Perspective, J Athl Enhanc Vol: 13 Issue: 2
An Overview on Sports Nutrition and its Key Principles
Alex Jack*
1Department of Sport Psychology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, USA
*Corresponding Author: Alex Jack,
Department of Sport Psychology, University
of New Mexico, Albuquerque, USA
E-mail: jackalex12@unm.edu
Received date: 26 February, 2024, Manuscript No. JAE-24-134602;
Editor assigned date: 29 February, 2024, PreQC No. JAE-24-134602 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 14 March, 2024, QC No. JAE-24-134602;
Revised date: 21 March, 2024, Manuscript No. JAE-24-134602 (R);
Published date: 28 March, 2024, DOI: 10.4172/2324-9080.1000120
Citation: Jack A (2024) An Overview on Sports Nutrition and its Key Principles. J Athl Enhance 13:2.
Description
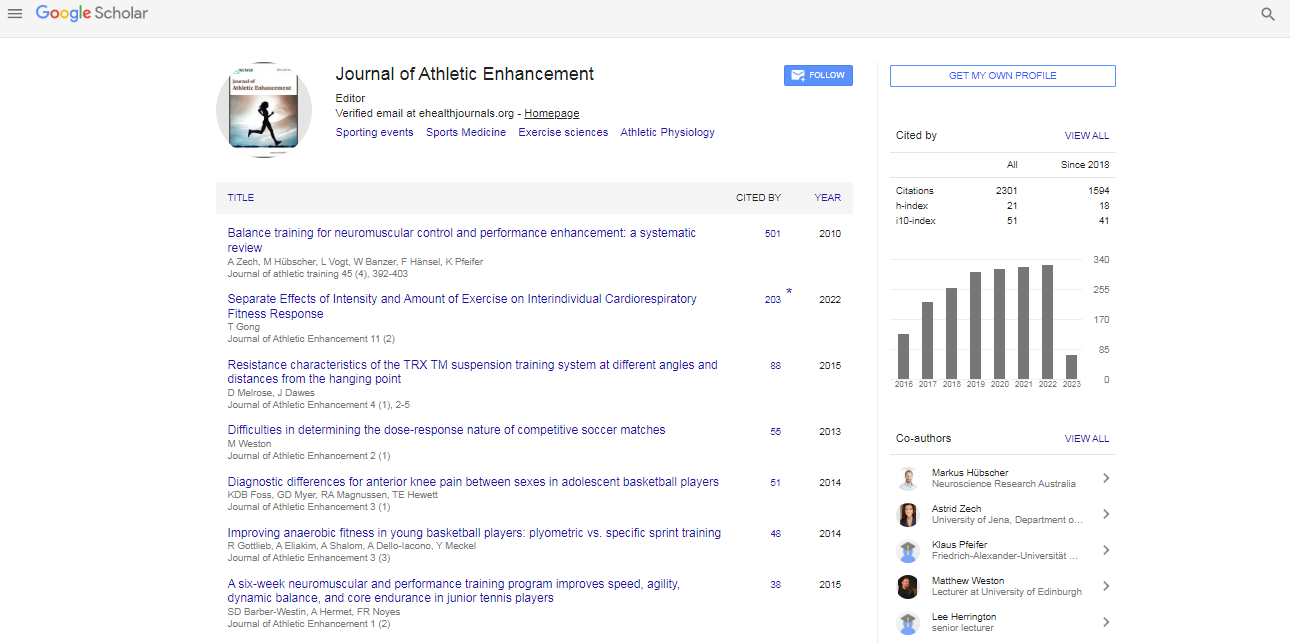
Sport nutrition plays a pivotal role in optimizing athletic performance and maintaining overall health for athletes across various disciplines. It encompasses the science of nourishment tailored to meet the unique physiological demands of athletes, focusing on enhancing performance, supporting recovery, and reducing the risk of injuries.
Key principles of sports nutrition
Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the primary macronutrients essential for fueling energy production, muscle repair, and metabolic functions. The distribution of macronutrients in an athlete’s diet varies based on individual goals, training intensity, and sport-specific requirements.
Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for optimizing performance and preventing dehydration-induced fatigue and impaired cognitive function. Athletes must maintain fluid balance by consuming water and electrolytes before, during, and after exercise sessions, with intake adjusted based on sweat rate and environmental conditions.
Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals play critical roles in various physiological processes, including energy metabolism, immune function, and tissue repair. Athletes should prioritize a diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to ensure adequate micronutrient intake.
Timing: Proper timing of nutrient intake is essential for maximizing performance and facilitating recovery. Pre-exercise meals should provide sustained energy, while post-exercise nutrition should focus on replenishing glycogen stores, repairing muscle tissue, and promoting recovery.
Nutrient requirements for athletes
Carbohydrates: As the primary fuel source for high-intensity exercise, carbohydrates are essential for sustaining energy levels and optimizing performance. Athletes should aim to consume adequate carbohydrates, prioritizing complex sources such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to support sustained energy release.
Proteins: Protein is crucial for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance, especially during periods of intense training or competition. Athletes should aim to distribute protein intake evenly throughout the day, focusing on high-quality sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy, legumes, and plant-based proteins.
Fats: While often overlooked, dietary fats play key roles in hormone production, cellular function, and energy metabolism. Athletes should prioritize healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish to support overall health and performance.
Hydration: Optimal hydration is essential for maintaining performance and preventing dehydration-related complications such as heat illness and impaired cognitive function. Athletes should monitor their fluid intake and aim to consume adequate fluids before, during, and after exercise, adjusting based on sweat rate and environmental conditions.
Dietary strategies for athletes
Meal planning: Structured meal planning ensures that athletes meet their nutrient needs while optimizing performance and recovery. Athletes should aim for balanced meals containing a combination of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, with timing tailored to training schedules and individual preferences.
Nutrient timing: Strategic nutrient timing can enhance performance and recovery by providing the body with the fuel and building blocks it needs at the right times. Pre-exercise meals should focus on carbohydrates for energy, while post-exercise nutrition should include a combination of carbohydrates and proteins to replenish glycogen stores and support muscle repair.
Supplementation: While whole foods should always be the primary source of nutrients, targeted supplementation may be beneficial for athletes with specific needs or deficiencies. Common supplements used by athletes include protein powders, creatine, betaalanine, and electrolyte replacements, although individual responses may vary.
Individualization: It's essential to tailor nutrition strategies to individual athletes based on factors such as age, gender, body composition, training volume, and sport-specific demands. Working with a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist can help athletes develop personalized nutrition plans to optimize performance and overall well-being.
Sport nutrition is a cornerstone of athletic performance, providing athletes with the fuel, nutrients, and hydration needed to excel in their chosen sports while supporting overall health and well-being. By understanding the key principles of sports nutrition, meeting nutrient requirements, and implementing dietary strategies tailored to their individual needs, athletes can optimize performance, accelerate recovery, and achieve their full potential on and off the field.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi