Case Report, Clin Oncol Case Rep Vol: 6 Issue: 6
Acquired MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation and Complex Mutations in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report
Patricia Cordeiro Gonzalez*, Joaquin Mosquera Martinez, Manuel Fernandez Bruno, Beatriz Alonso de Castro, Rosario Garcia Campelo
Department of Medical Oncology Service, University Hospital A Coruna, As Xubias, s/n, A Coruna, 15006, Spain.
*Corresponding Author: Patricia Cordeiro Gonzalez
Department of Medical Oncology Service, University Hospital A Coruna, As Xubias, s/n, A Coruna, 15006, Spain.
E-mail: patricia.cordeiro.gonzalez@sergas.es
Received: April 03, 2023; Manuscript No: COCR-23-93914;
Editor Assigned: April 04, 2023; PreQC Id: COCR-23-93914 (PQ);
Reviewed: April 13, 2023; QC No: COCR-23-93914 (Q);
Revised: April 16, 2023; Manuscript No: COCR-23-93914 (R);
Published: April 21, 2023; DOI: 10.4172/cocr.6(4).285
Citation: Gonzalez PC, Martinez JM, Bruno MF, de Castro BA, Campelo RG (2023) Acquired MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation and Complex Mutations in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report. Clin Oncol Case Rep 6:4
Abstract
We report an EGFR NSCLC patient with progression disease to Osimertinib due to METΔex14 mutation. As exon 21 L858R substitution was still detected, the patient was treated with the combination of Osimertinib and Capmatinib. After 3 months, radiological progression disease and C797S and V802F as new on target mutations were detected, so Gefitinib was administered in monotherapy, with patient exitus due to neumothorax secondary to massive cavitation of his lung cancer 3 months later.
Keywords: Osimertinib; Capmatinib; MET exon 14 skipping; C797S mutation; Case report
Introduction
Activating mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) gene cause 10% to 20% of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC); and approximately in 90% of this cases, exon 19 deletions and exon 21 L858R substitutions are detected [1,2].
Those aberrations are succesfully targeteated with EGFR Tirosin Quinase Inhibitors (EGFR-TKI). However, acquired resistance due to heterogeneous mechanisms is inevitable [3]. The escape tumoral strategy can be on-target, like EGFR C797S or V802F mutations; and off-target, like MET dysregulation [3].
We present an EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma with longterm survivorship thanks to personalized medicine. Among other particularities, this case is unique due to anomalous resistance mechanisms, such as MET exon 14 skipping mutation (METΔex14), and the highly-personalized sequence of target therapies used.
Case Presentation
A fragile 80 years old patient with hypertension, diabetes and mild renal failure with pleuritic pain, asthenia and dyspnea is diagnosed by CT guided biopsy of a lung adenocarcinoma with liver and bone metastasis, with EGFR exon 21 L858R substitution (cobas®EGFR PCR test).
Our patient receives Osimertinib 80 mg every 24 hours, with excellent tolerance and partial response, until radiological progression 13 months later. However, due to clinical benefit, the patient continues therapy 5 months more until deterioration due to bone pain and asthenia. Them, a new biopsy guided by Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) was performed, and AmoyDx® Pan Lung Cancer PCR Panel detects the primary mutation (L858R of exon 21), and METΔex14 as off-target escape mechanism. The limited tumour specimen does not allow additional molecular studies, so Capmatinib (400 mg every 12 hours) is added to Osimertinib.
During the combination treatment, the patient presents grade 1 asthenia, peripheral edema, and worsening of his renal impairment, requiring discontinuation of Capmatinib on one occasion.
Finally, disease progression is confirmed 3 months later, requiring hospital admission due to dyspnea and pain. Meanwhile, a liquid biopsy (GUARDANT 360®) detects the new EGFR complex mutation C797S and V802F, as well as exon 21 L858R substitution.
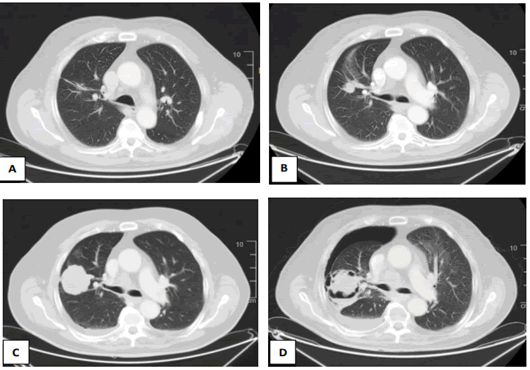
In this context, the patient starts Gefinitib 250 mg every 24 hours, presenting a clinical improvement, without pain and toxicities; until admission 3 months later due to a massive necrosis and cavitation of the pulmonar mass, with secondary hydropneumothorax (Figure 1), which finally causes patient exitus, despite of urgent chest drainage.
Figure 1: CT scans of the pulmonar mass. (A) spiculated left lung nodule at baseline. (B) Proggressive disease after 13 months of response to Osimertinib. (C) Proggresion of a Solid mass after Osimertinib and Capmatinib treatment. (D) massive cavitation with secondary hydroneumothorax during Gefitinib Treatment.
Discussion
METΔex14 is detected in 3% to 4% and MET amplification in 1 to 6% of NSCLC at debut and in 5% to 50% of EGFR mutant NSCLC as resistance mechanism [3, 4]. In both cases, Capmatinib, a selective inhibitor of MET receptor, has shown substantial antitumour activity in “GEOMETRY mono-1” clinical trial.
Furthermore, the promising combination of Osimertinib and Capmatinib is being tested in the on-going trial GEOMETRY-E. In the literature, few cases of this association has been presented, especially with METΔex14 as escape mechanism [5]. We decided to offer this novel combination due to the previous tolerance to Osimertinib and the risk of hyperprogression if inhibiting MET receptor exclusively when L858R mutation is still detected.
C797S mutation is poorly characterized yet, but it is estimated to happen in up to 26% of NSCLCs after EGFR-TKI treatment. CT97S mutation is maybe the main mechanism of escape to Osimertinib (7% in FLAURA study, 15% in real world data), and the second to 1º and 2º generation EGFR-TKI [6]. To date, no standard treatment has been defined but there is preclinical and clinical data supporting treatment with 1st and 2nd generation EGFR-TKI. In this setting, we decide to change Osimertinib therapy to Gefinitib, and Capmatinib disruption is supported in our case due to progression, bad tolerance and no detection of METΔex14 in liquid biopsy. With Gefinitib, the patient presents few months of general improvement, but massive necrosis causes ultimately its death, even when the cavitation of the tumour could have been secondary to EGFR-TKI response.
Conclusion
The unquestionable consolidation of Osimertinib in 1st line of EGFR NSCLC after FLAURA trial has generated a delicate scenario when finally progression disease take place. Time and clinical trial results are needed to reach consolidated scientific evidence, but meanwhile oncologist must take hard therapeutical decisions due to novel mutations mechanism and new agents.
Meanwhile biomarked-directed clinical trial with multiarm designs as ORCHARD are still recruiting, data of case reports is especially interesting. In this scenario, we report a rare case of a patient with EGFR NSCLC with adquired resistance due to METΔex14 treated with Capmatinib and Osimertinib in combination, and posterior C797S mutation treated with Gefinitib (Table 1). To our knowledge, this could be the first report of this sequence of mutations and treatments.
Table 1: squema of treatments administered, with molecular findings and the specific response to each line
| Treatment | Best response | Molecular results | Sample | Sample and molecular analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib | Partial response, Progressive disease | EGFR exon 21 L858R substitution | Tumor | Cobas®EGFR PCR test |
| Osimertinib + Capmatinib | Progressive disease | EGFR exon 21 L858R substitution | Tumor | AmoyDx® Pan Lung Cancer PCR Panel |
| METΔex14 | ||||
| Gefitinib | Proggressive disease | EGFR complex mutation C797S and V802F | Plasma | GUARDANT 360® |
| EGFR exon 21 L858R substitution | ||||
Conficts of interests
There are not research supports or conflicts of interest related to this publication.
Ethics Statement
We confirm that the patients gave informed consent to publish his clinical and radiological images.
References
- Zhang T, Wan B, Zhao Y, Li C, Liu H, et al. (2019) Treatment of uncommon EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: New evidence and treatment. Translat Lung Can Res 8: 302. [Google Scholar] [Cross Ref]
- Harrison PT, Vyse S, Huang PH (2020) Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Seminars Cancer Biol 61: 167-179. [Google Scholar] [Cross Ref]
- Zeng Y, Yu D, Tian W, Wu F (2022) Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib and emerging therapeutic strategies in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Current Opinion Oncol 34: 54-65. [Google Scholar] [Cross Ref]
- Wu YL, Zhang L, Kim DW, Liu X, Lee DH, et al. (2018) Phase Ib/II study of capmatinib (INC280) plus gefitinib after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET factor-dysregulated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 36: 3101. [Google Scholar] [Cross Re]
- Takamori S, Seto T, Yamaguchi M, Kinoshita F, Fujishita T, et al. (2022) Success of tepotinib therapy in overcoming resistance to osimertinib in a patient with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma with a potential acquired MET exon 14 skipping mutation. Fron Oncol 5715. [Google Scholar] [Cross Ref]
- Dong RF, Zhu ML, Liu MM, Xu YT, Yuan LL, et al. (2021) EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: From molecular mechanisms to clinical research. Pharmacol Res 167:105583. [Google Scholar] [Cross Ref]
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi