About the Journal of Nuclear Energy Science & Power Generation Technology

Scopus Coverage 2018
Archived inInternational Nuclear Information System Repository (IAEA.org)
Journal of Nuclear Energy Science & Power Generation Technology (JNPGT) is an open access, Scopus indexed journal with a primary objective to provide research and applications related to Nuclear Energy and Power generation. The journal provides the choice of both open access and subscription mode of publication to the authors and publishes almost all types of write-ups like research articles, review, case reports, case study, commentary, letter to editor, mini review, opinion, short communication, book review, s etc. The scope of the journal mainly focuses on Nuclear energy science, nuclear power generation, nuclear materials, advance nuclear reactors, reactor safety, nuclear waste management, radioactivity, atomic energy, production and control of radioisotopes and labeled compounds, electric, hydro, coal and gas based power generation etc.
The authors can submit their manuscript through Online Submission System. If the authors find any difficulty in submitting their manuscript,
E-mail it topublisher@scitechnol.com
The journal follows double blind peer review process. Manuscripts submitted by authors will be evaluated on Tracking System by Editors & reviewers of particular expertise in the same field to ensure that the published articles are of high quality with accurate and reliable information & data, which reflect solid scholarship. Editors can manage the whole submission, review, revision and publishing process, however at least two independent reviewer's approval followed by the Editor is required for the acceptance of any citable manuscript.
2018 Journal Impact Factor is the ratio of the number of citations achieved in the year 2018 based on Google Search and Google Scholar Citations to the total number of articles published in the last two years i.e. in 2016 and 2017. Impact factor measures the quality of the Journal.
If ‘X’ is the total number of articles published in 2016 and 2017, and ‘Y’ is the number of times these articles were cited in indexed journals during 2018 then, impact factor = Y/X.
The following classifications and topics related with it will be considered for publication in JNPGT.
Nuclear Power Generation
The nuclear power generation can be done in a power plant in which heat source comes from one or more nuclear reactors or even may be utilizing the steam by connecting it to a generator.
Power Generation Technology
The technique of generating power or energy in any form by exhausting the fuel or nucleus are termed as power generation technology. This technology is used in power stations using electromechanical generators.
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts mechanical power into electrical power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. Most power stations contain one or more generators, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into three-phase electric power. The relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor creates an electrical current. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Cleaner sources include nuclear power, and an increasing use of renewables such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric.
Quantum physics including quantum field theory, is a fundamental theory in physics which describes nature at the smallest – including atomic and subatomic – scales. It underlies the mathematical framework of many fields of physics and chemistry, including atomic physics, molecular physics, particle physics, nuclear chemistry, and nuclear physics. Quantum theory is needed for understanding nuclear structure.
Nuclear Energy
The energy which are emitted after the nuclear fission or fusion of two nucleus are termed as nuclear energy. The nuclear energy are artificially obtained in nuclear reactors and have many uses.
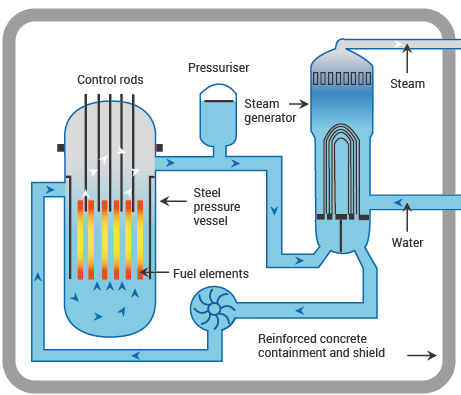
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a self-sustained nuclear chain reaction. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. In a nuclear power reactor, the energy released is used as heat to make steam to generate electricity. The principles for using nuclear power to produce electricity are the same for most types of reactor. The energy released from continuous fission of the atoms of the fuel is harnessed as heat in either a gas or water, and is used to produce steam.
Computational Fluid Dynamics
The branch of fluid mechanics which deals with the numerical analysis and algorithms to solve the problems involving fluid flow are termed as Computational Fluid Dynamics. It utilizes applied mathematics, physics and computational software.
Nuclear Accidents
The accidents which occur in the nuclear power plant involving the nuclear reactor and causes significant consequesnces to the peoples lives, to the environment & the facility are termed as nuclear accidents.
Fuel Cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle refers to the progression of nuclear fuel through different atages from front end to the back end. If the spent fuel is reprocessed, it is called closed fuel cycle and if not reprocessed, then called open fuel cycle.
Hydroelectric Power
The power station in which electricity is generated by using hydropower is termed as hydroelectric power station. It is widely used source of renewable energy. The Asia-pacific region genearates 32% of the global hydropower. The energy or power which is obtained at the end is termed as hydroelectric power.
Thermal Power
The kind of power plant in which the steam is utilized to run a turbine which in turn drives an electrical generator is termed as Thermal Power Stations. Generally fossil fuel resources are used to get the water heated & become steam. The power which is obtained as a result is termed as thermal power.
Thermonuclear Energy
The energy obtained after nuclear fusion or fission of atomic nuclei at very high temperature is termed as thermonuclear energy. The energy emitted is a rich source of power & is termed as atomic energy. A common example is hydrogen bomb.
Nuclear Power Plant Design
The design of a nuclear power plant is very crucial & differs vastly depending upon its type & need. The optimization & scale up is also very important and propoer information might save a lot of cost for the engineers.
Nuclear Reactor Safety
The nuclear reactor safety is very important in accordance with the people lives associated with it. The safety protocols to be audited in a timely manner. It requires intelligent planning, proper design with conservative margins and back-up systems, high-quality components and a well-developed safety culture in operations.
Reactor Design
The design of a reactor is very crucial & differs vastly depending upon its type & need. The optimization & scale up is also very important and propoer information might save a lot of cost for the engineers.
Reactor Engineering
Reactor Engineering refers to the engineering works carried out in a nuclear reactor to make the reactor available at its optimum working state as well as to prevent any situations or danger involving the fission process.
Fusion Research
The research involving the joining of two molecules after colliding at a very high speed are called fusion research. Here at the end a new type of atomic nucleus is formed after fusion of two nucleus.
Nuclear Security
Nuclear security deals with the prevention, response to the unauthorized access, theft, sabotage or an illegal transfer involving the nuclear materials. It also takes care of the propoer disposal of radioactive & nuclear wastes to make sure the well being of society.
Nuclear Waste Management
The management of the wastes which are generated or remained as a by product or useless product after nuclear fission are termed as nuclear wastes. Generally most of them are radioactive.
Radioactive Waste Management
The management of the wastes materials which semits radiations or containing radionuclides. Depending on their radiation levels they could be divided as high level, low level, radioactive material.
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is the branch of physics which deals with the study of the constituents of atomic nuclei, their structure, behaviour & their interaction to generate the nuclear energy.
Nuclear Chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of radioactivity, nuclear transmutation & processes. It also involves the study of the propoerties of the nuclear materials at different stages.
Nuclear Materials
The materials hich are associate with or utilized in the process of nuclear energy or power generation are termed as nuclear materials. These are generally metals like uranium, plutonium, thorium etc.
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
Journal of Nuclear Energy Science & Power Generation Technology is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.
Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi