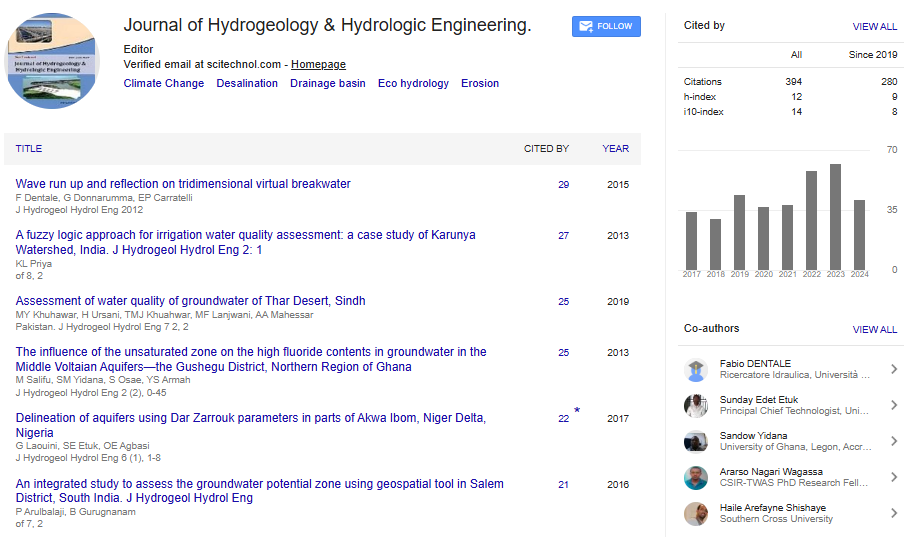
Editorial, J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng Vol: 1 Issue: 1
In-situ Remediation of Shallow Aquifer Pollution
| Huan Feng1* and Michael A. Nwachukwu2 | |
| 1Department of Earth & Environmental Studies, Montclair State University, Montclair New Jersey 07043, USA | |
| 2Department of Environmental Technology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria | |
| Corresponding author : Huan Feng, PhD, Professor Department of Earth & Environmental Studies, Montclair State University, Montclair New Jersey 07043, USA E-mail: fengh@mail.montclair.edu |
|
| Received: August 06, 2012 Accepted: August 07, 2012 Published: August 09, 2012 doi:10.4172/2325-9647.1000e103 | |
| Citation: Feng H, Nwachukwu MA (2012) Should Dispersants be Used to Alleviate the Impact of a Marine Oil Spill?. J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng 1:1 doi:10.4172/jhhe.1000e103 |
Abstract
In-situ Remediation of Shallow Aquifer Pollution
Improvement of urban and rural infrastructure such as road construction in particular in many developing countries has increased pollution stress on groundwater quality. For example, borrow pits from where materials were collected for road projects are usually abandoned instead of reclaimed. Soon after, these abandoned borrow pits become urban waste disposal pits. Aquifer pollution stress arises as the pits become point sources of groundwater pollution in the area or regions where water table is near surface. Again, lack of storm water management during road construction and other open engineering sites such as mechanic villages causes continuous enrichment of pollutants, such as toxic metals and organics, in surface water and groundwater.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi