About the Journal

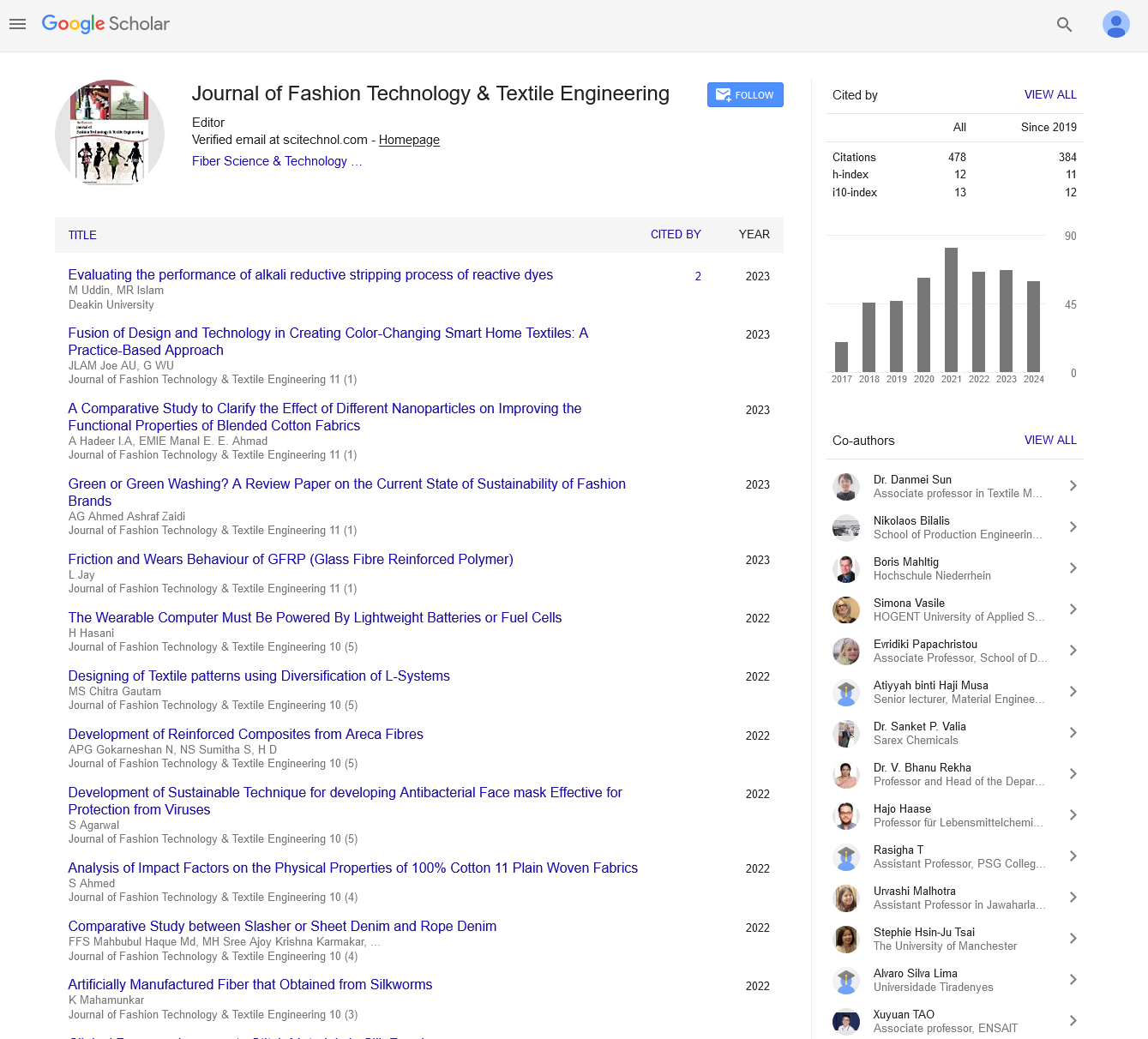
Journal of Fashion Technology & Textile Engineering (ISSN: 2329-9568) is a peer-reviewed scholarly journal and aims to publish the most complete and reliable source of information on the discoveries and current developments in the mode of original articles, review articles, case reports, short communications, etc. in all major themes pertaining to advances in fashion technology & improved understanding of textile manufacturing and making them available online freely without any restrictions or any other subscriptions to researchers worldwide.
Journal of Fashion Technology & Online Submission System Engineering focuses on the topics that include:
- Fiber Science & Technology
- Textile Materials
- Clothing/ Apparel Technologies
- Studies on Colors & Dyes
- Aestethics of Textile
- Textile Finishing and Treatment
- Fashion Designing & Marketing
- Nanotechnology in textile Research
- Wearable Electronics
- e-Textiles
- Multifunctional Materials
- Modelling and Simulation
Review processing is performed by the editorial board members of Journal of Fashion Technology & Online Submission System Engineering or outside experts; at least two independent reviewers approval followed by editor approval is required for acceptance of any citable manuscript. Authors may submit manuscripts and track their progress through the online tracking system, hopefully to publication.
Confirmed Special Issues:
- 3D and 4D printing in Textiles and Clothing
- Wearable Technology: From the Single Elements to the Integrated Systems
Online Submission System or send as an e-mail attachment to us at submissions@scitechnol.com
Fibre Science
Fibre Science and Technology dwells on the science and technology of natural and man-made fibres. It integrates the vast subject domain from the viewpoint of material science and technology. Further, it accords a special reference to fibres and textiles, which constitute a major class of polymeric materials.
Textile Materials
Textiles can be made from many materials. These materials come from four main sources: animal (wool, silk), plant (cotton, flax, jute), mineral (asbestos, glass fibre), and synthetic (nylon, polyester, acrylic). In the past, all textiles were made from natural fibres, including plant, animal, and mineral sources.
ClothingTechnology
It is a multimedia learning system that provides fundamental underpinning knowledge on the manufacture of apparel.
Colors & Dyes
These studies include the functions, properties, method of manufacture, origin of various colours and dyes that are used in the textile manufacture.
Fabric Textile
Fabric aesthetic character is defined as a relationship among a minimum of six concepts: style, body, cover, surface, texture, drape, and resilience. These concepts can be described by how they are subjectively perceived, by possible sub concepts by objective tests.
Textile Finishing
Finishing processes can be divided into two broad classes: physical and chemical. In most cases finishing comprises 3 stages: washing and drying, stabilising and Pressing and aesthetics.
Fashion Design & Marketing
Fashion design is defined by the creators of new footwear, clothing and accessories. Fashion designing involves a set of skills that range from market research and creativity to sketching and fabric selection.
Nanotechnology in Textile
Nanotechnology at the molecular level can be used to develop desired textile characteristics, such as high tensile strength, unique surface structure, soft hand, durability, water repellency, fire retardancy, antimicrobial properties.
Wearable Electronics
Wearable electronics are clothing and accessories incorporating computer and advanced electronic technologies. The designs often incorporate practical functions and features, but may also have a purely critical or aesthetic agenda.
e-Textiles
e-textiles, also known as smart garments, smart clothing, electronic textiles, smart textiles, or smart fabrics, are fabrics that enable digital components (including small computers), and electronics to be embedded in them.
3D Fabrics
These are the fabrics in which yarn runs through the braid in all three directions, formed by inter-plaiting three orthogonal sets of yarn. The fiber architecture of three-dimensional braided fabrics provides high strength, stiffness, and structural integrity, making them suitable for a wide array of applications.
Smart Textiles
Fabrics that purify water using nothing but the sun as energy source. Clothes that can take an ECG or become cool at extreme temperaturas are known as Smart textiles.
Technical Textiles
Technical textiles include textiles for automotive applications, medical textiles (e.g., implants), geotextiles (reinforcement of embankments), agrotextiles (textiles for crop protection), and protective clothing.
Fashion Theory
It covers the study of fashion, including aspects from sociology, art history, consumption studies, and anthropology. It also includes studies on practices of production, dissemination, and consumption of dress.
Fashion History
The history of fashion design refers to the development of the fashion industry which designs clothing and accessories. The modern industry is based around firms or fashion houses run by individual designers, started in the 19th century with Charles Frederick Worth who was the first designer to have his label sewn into the garments that he created.
Fashion Design
Fashion Design is the art of application of design and aesthetics or natural beauty to clothing and accessories. Fashion design is influenced by cultural and social latitudes and has varied over time and price.
Fashion Marketing
Fashion marketing is part of the business side of the fashion industry, and it is just as important as the creative side of a fashion house. Even if you have a great product, it won't go far unless you do a significant marketing to create awareness.
Fashion Branding
The process involved in creating a unique name and image for a product in the consumers’ mind, mainly through advertising campaigns with a consistent theme is called fashion branding. Branding aims to establish a significant and differentiated presence in the market that attracts and retains loyal customers.
Multifunctional Materials
Multifunctional Material is defined to be any material or material-based system which integrally combines two [or possibly more] properties, one of which is normally structural and the other functional, e.g. optical, electrical, magnetic, thermal etc...
Textile Composites
Textile composites are fiber-reinforced composite materials, the reinforcement being in the form of a textile fabric (woven, knitted, braided).
2017 Journal Impact Factor is the ratio of the number of citations achieved in the year 2017 based on Google Search and Google Scholar Citations to the total number of articles published in the last two years i.e. in 2015 and 2016. Impact factor measures the quality of the Journal.
If ‘X’ is the total number of articles published in 2015 and 2016, and ‘Y’ is the number of times these articles were cited in indexed journals during 2017 then, impact factor = Y/X.
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
Journal of Fashion Technology & Textile Engineering is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.
Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi